Gamma Ray Waves Facts

Gamma rays Everything you need to know Space
Gamma radiation (gamma rays) refers to the part of the electromagnetic spectrum with the most energy and shortest wavelength. Astrophysicists define gamma radiation as any radiation with an energy above 100 keV. Physicists define gamma radiation as high-energy photons released by nuclear decay. Using the broader definition of gamma radiation.
Jenis Radiasi Pengion dan Nonpengion, Partikel
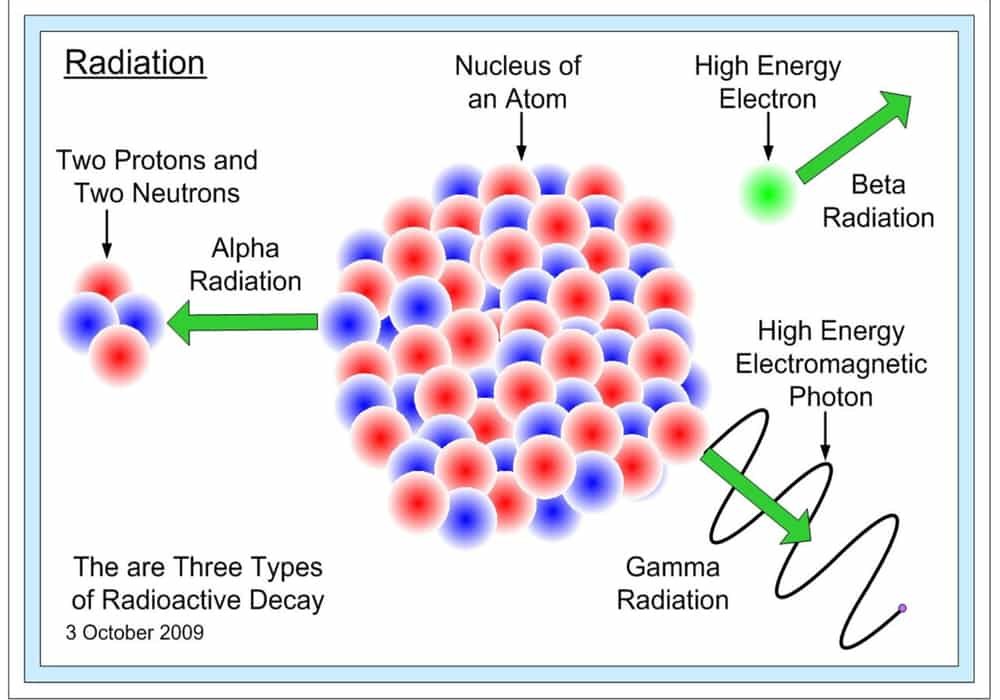
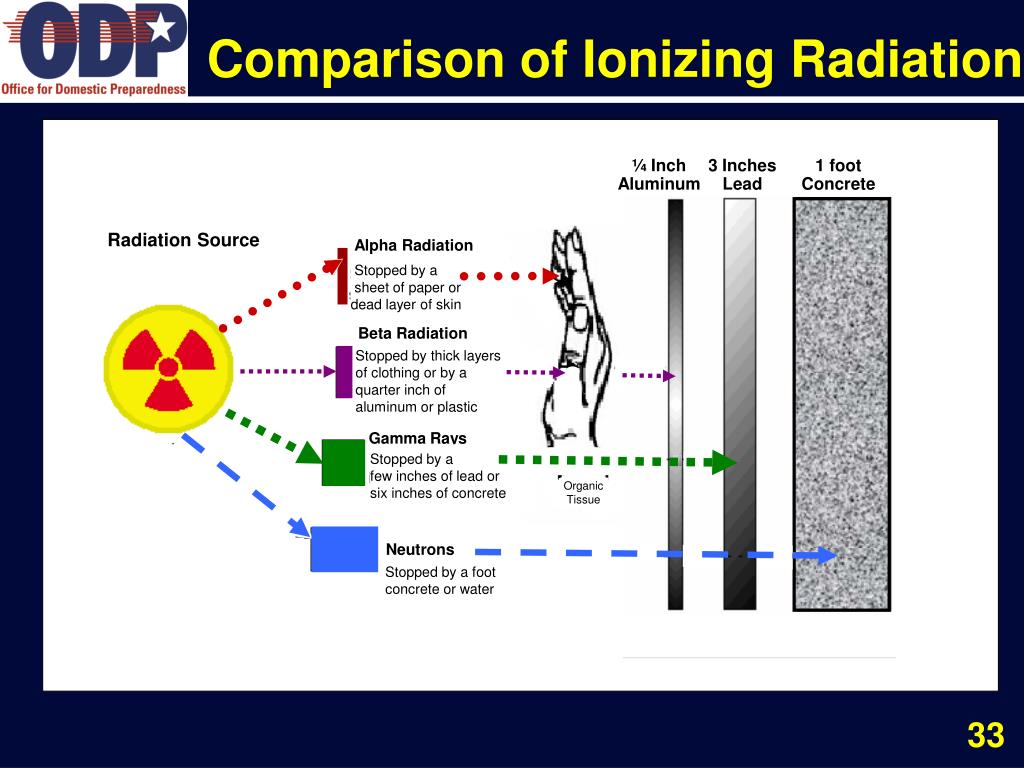
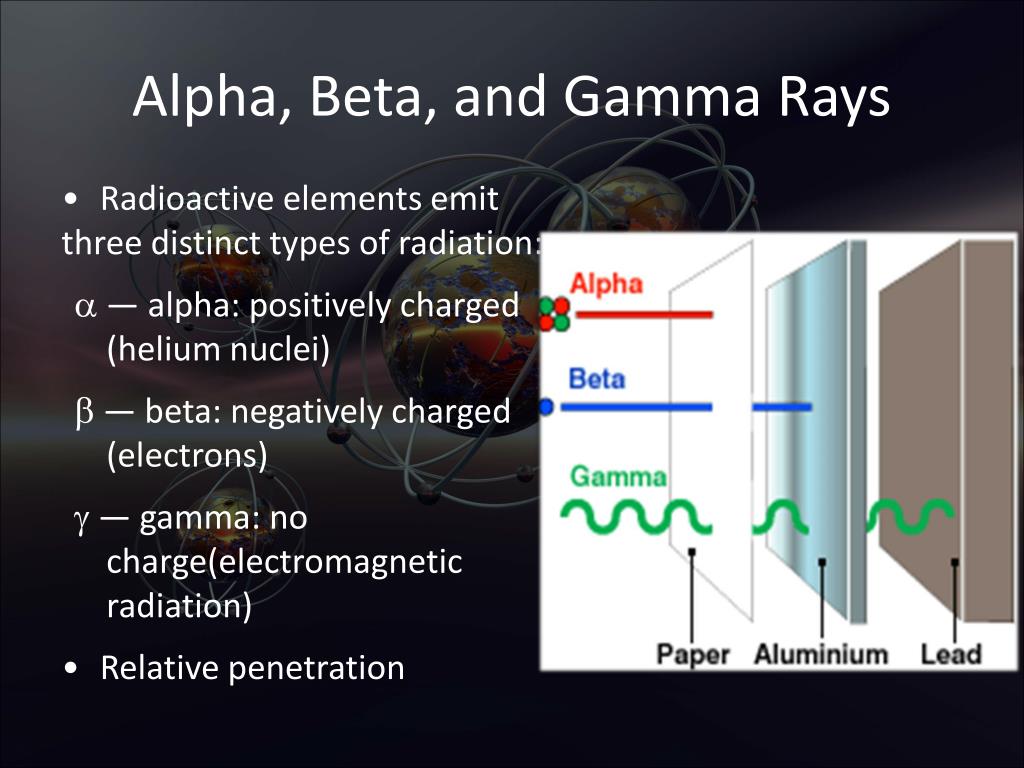
Gamma rays. Six years after the discovery of radioactivity (1896) by Henri Becquerel of France, the New Zealand-born British physicist Ernest Rutherford found that three different kinds of radiation are emitted in the decay of radioactive substances; these he called alpha, beta, and gamma rays in sequence of their ability to penetrate matter. The alpha particles were found to be identical with.

Gamma Ray Waves Facts
7.3.1 Basic Principles. Gamma ray emission imaging looks at gamma rays emitted from within an object to provide an image of the location of emission of the gamma rays inside the object. The general idea is illustrated in Fig. 7.4. The imaging device is most often called a "camera" or "scanner". Fig. 7.4.
What is Radiation? IAEA
Gamma rays are produced primarily by four different nuclear reactions: fusion, fission, alpha decay and gamma decay. Nuclear fusion is the reaction that powers the sun and stars. It occurs in a.
GammaRay Burst Introduction
Gamma-ray wavelengths are so short that they can pass through the space within the atoms of a detector. Gamma-ray detectors typically contain densely packed crystal blocks. As gamma rays pass through, they collide with electrons in the crystal. This process is called Compton scattering, wherein a gamma ray strikes an electron and loses energy.
Alpha Beta And Gamma Rays Comparison All About Radiation
Details regarding the gamma-ray imaging system, detector response characterization, image reconstruction algorithms, and uncertainty quantification are provided in the " Methods " section.
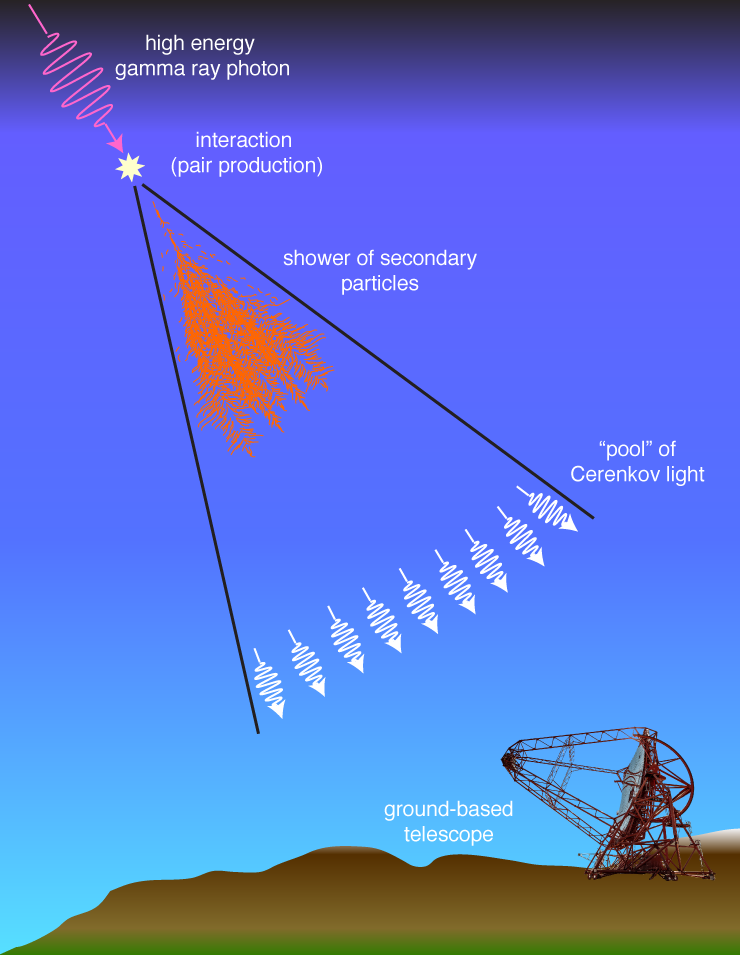
Imagine the Universe!
Since HEMI is a gamma-ray spectrometer it can resolve the energies of individual gamma rays to detect and identify specific radio-isotopes and to produce radiation maps associated with them. Due to its compactness, HEMI can be packaged in an environmental enclosure enabling completely autonomous operation including GPS/IMU, camera, and.
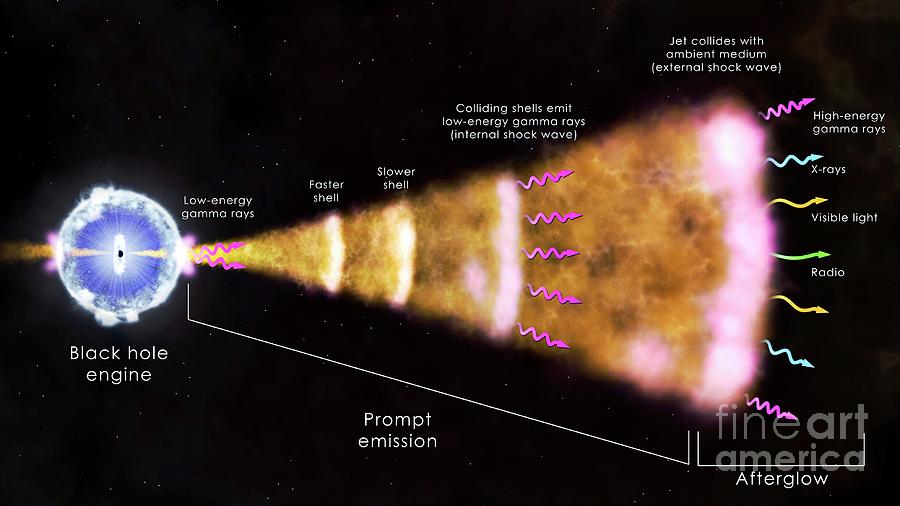
Gammaray Burst Mechanism Photograph by Nasa/goddard Space Flight Center/science Photo Library
Sinar gama. Sinar gama dipancarkan semasa pembelahan nuklear dalam letupan nuklear. Sinar gama (diwakili dengan huruf Yunani γ) merupakan bentuk sinaran elektromagnet (EMR) atau pancaran cahaya bagi frekuensi khas dihasilkan dari interaksi zarah sub-atom, seperti pelupusan elektron-positron dan penguraian radioaktif; kebanyakannya dihasilkan.
Gamma Rays Examples in Real Life StudiousGuy
Sinar gama. Ilustrasi emisi sinar gama ( γ) dari inti atom. Sinar gama dipancarkan selama fisi nuklir dalam ledakan nuklir. Sinar gama (sering kali dinotasikan dengan huruf Yunani gama, γ) adalah sebuah bentuk berenergi dari radiasi elektromagnetik yang diproduksi oleh radioaktivitas atau proses nuklir atau subatomik lainnya seperti.
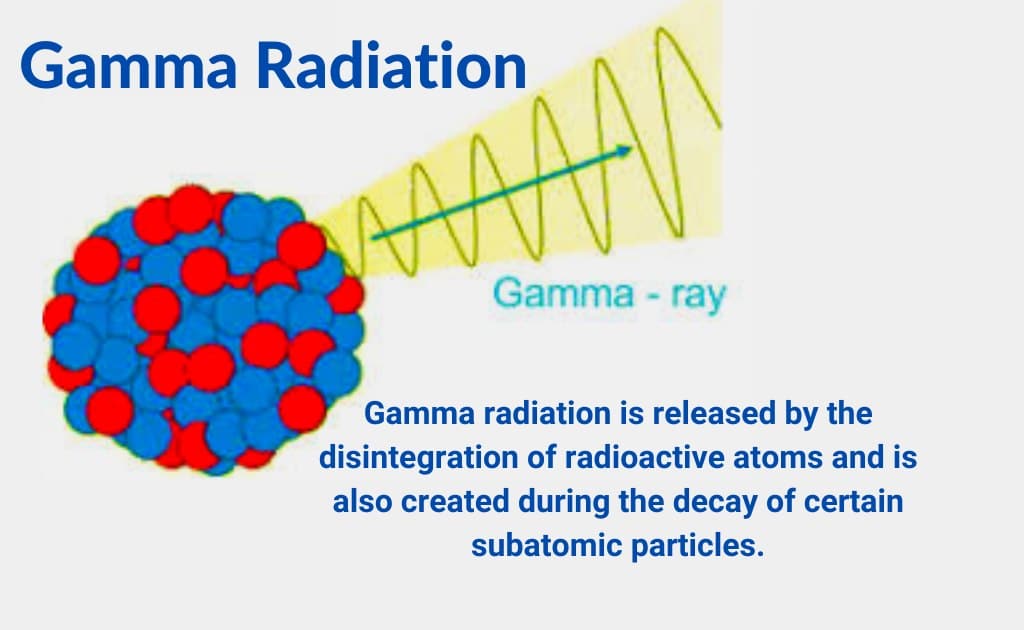
Gamma RadiationDefinition, Discovery, Sources, And Uses
The distinction between X-rays and gamma rays is not so simple and has changed in recent decades. According to the currently valid definition, X-rays are emitted by electrons outside the nucleus, while the nucleus emits gamma rays. Gamma rays frequently accompany the emission of alpha and beta radiation. Comparison of particles in a cloud chamber.

Lesson Gamma Radiation Nagwa
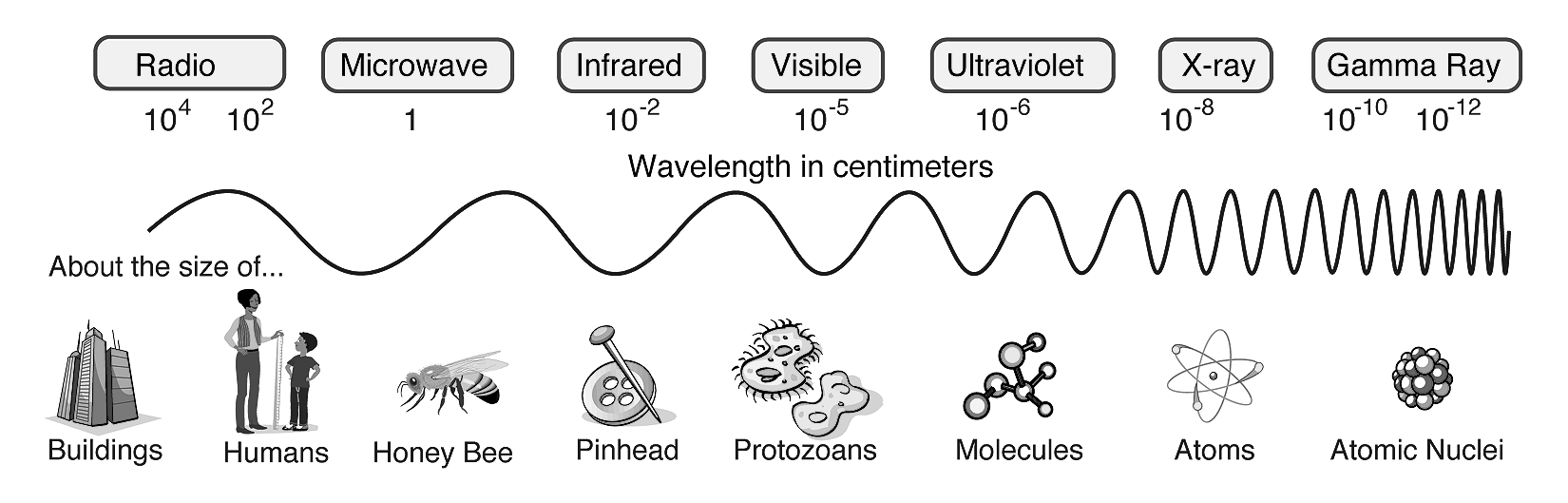
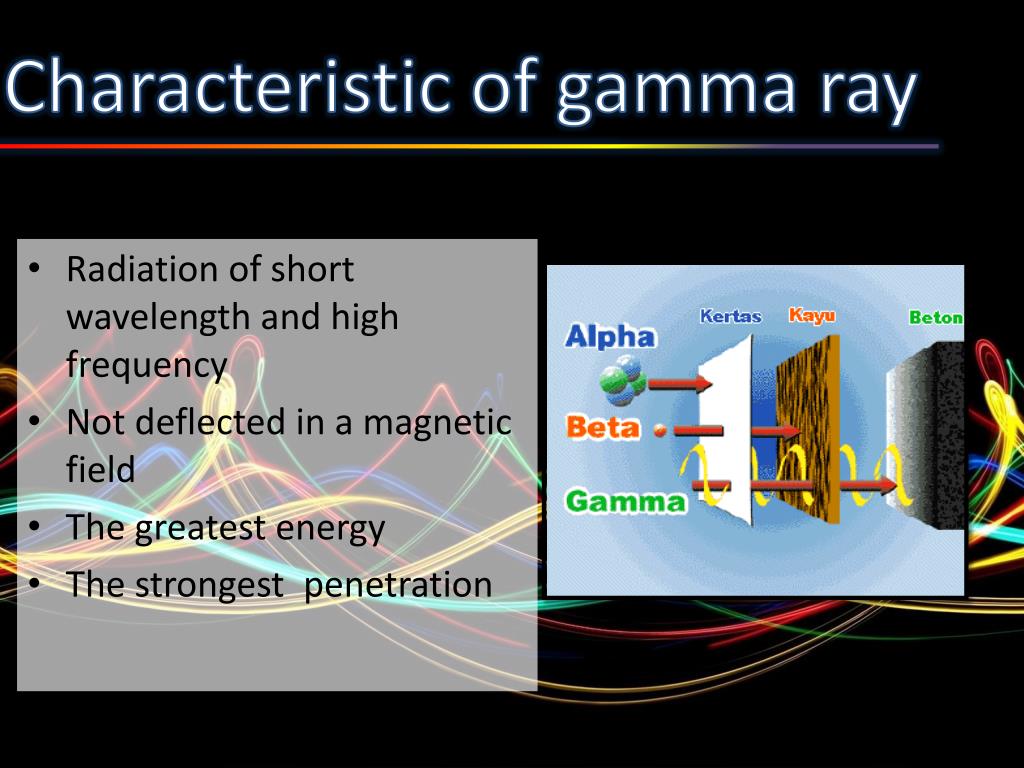
Characteristics. Shortest Wavelengths: Gamma rays have the shortest wavelengths and highest frequencies of all types of electromagnetic radiation. Highest Energy: Gamma rays have the highest energy of all electromagnetic radiation types, which allows them to penetrate most materials and cause significant damage to living tissues and structures.
PPT Atomic Nucleus and Radioactivity PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID7028434
gamma ray, electromagnetic radiation of the shortest wavelength and highest energy.. Gamma rays are produced in the disintegration of radioactive atomic nuclei and in the decay of certain subatomic particles.The commonly accepted definitions of the gamma-ray and X-ray regions of the electromagnetic spectrum include some wavelength overlap, with gamma-ray radiation having wavelengths that are.

radiation Gamma Rays, Photons, Wavelengths Britannica
Gamma Rays Attenuation. The total cross-section of interaction of a gamma rays with an atom is equal to the sum of all three mentioned partial cross-sections: σ = σf + σC + σp. Depending on the gamma ray energy and the absorber material, one of the three partial cross-sections may become much larger than the other two.
PPT GammaRay PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID6962017
Among the three, alpha is the weakest, and gamma is the strongest type of radiation. Gamma radiation or gamma ray is an extremely high-frequency radioactive radiation consisting of high-energy photons. It was first discovered by a French chemist and physicist, Paul Villard, in 1900. It was named gamma ray by Ernest Rutherford in 1903.
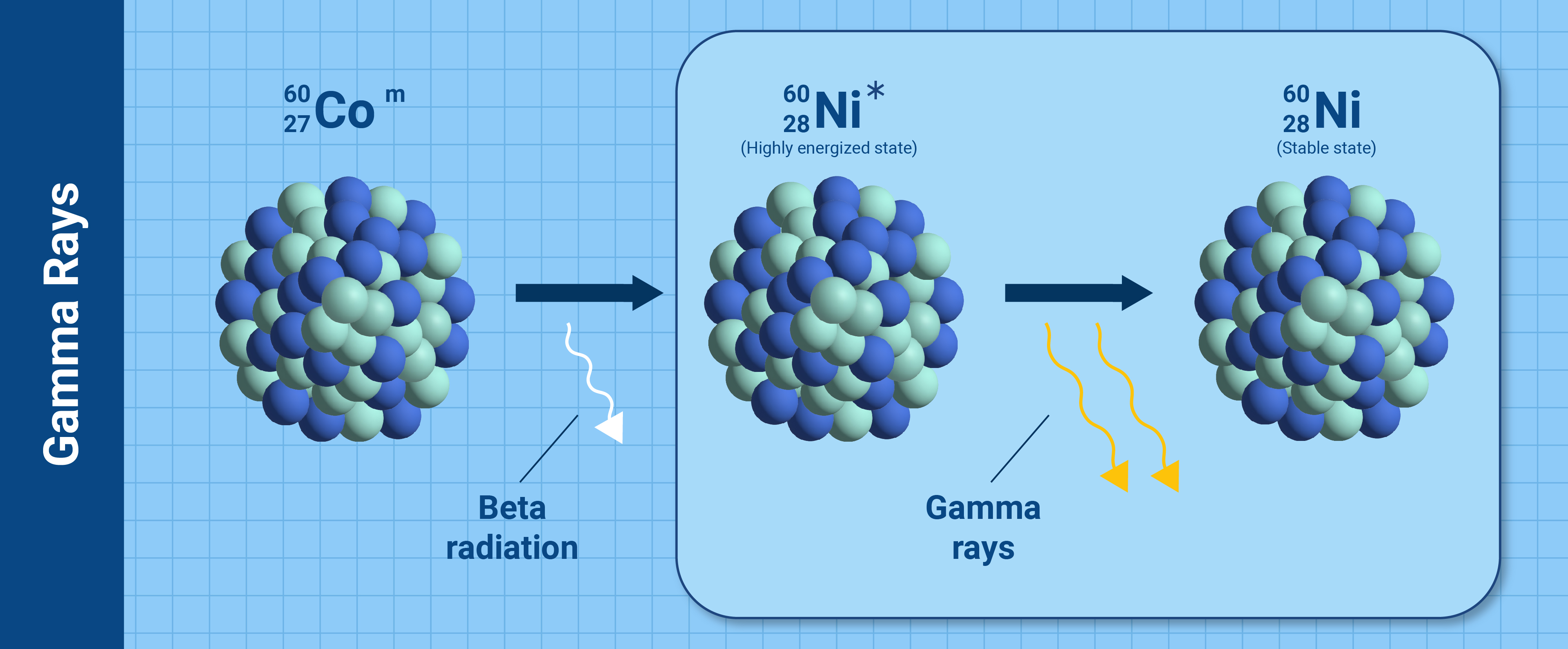
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/800px-Gamma_Decay.svg-589ce1fc3df78c475869d5bb.png)
What Is Gamma Radiation?
A gamma ray, also known as gamma radiation (symbol γ), is a penetrating form of electromagnetic radiation arising from the radioactive decay of atomic nuclei.It consists of the shortest wavelength electromagnetic waves, typically shorter than those of X-rays.With frequencies above 30 exahertz (3 × 10 19 Hz), each gamma ray imparts the highest photon energy of any form of electromagnetic.

Gamma Radiation and SPECT How radiation is used to maintain human health
This chapter deals with gamma background radiation that is exposed to two major natural sources: normal sources that are earthly gamma rays and astronomical rays. Earthbound gamma rays from radionuclide elements such as thorium, potassium, and uranium. Also, in building and enhancing materials such as medical plants, building purposes, some vegetables and fruits commonly used in markets and soil.