Sistem Integumen
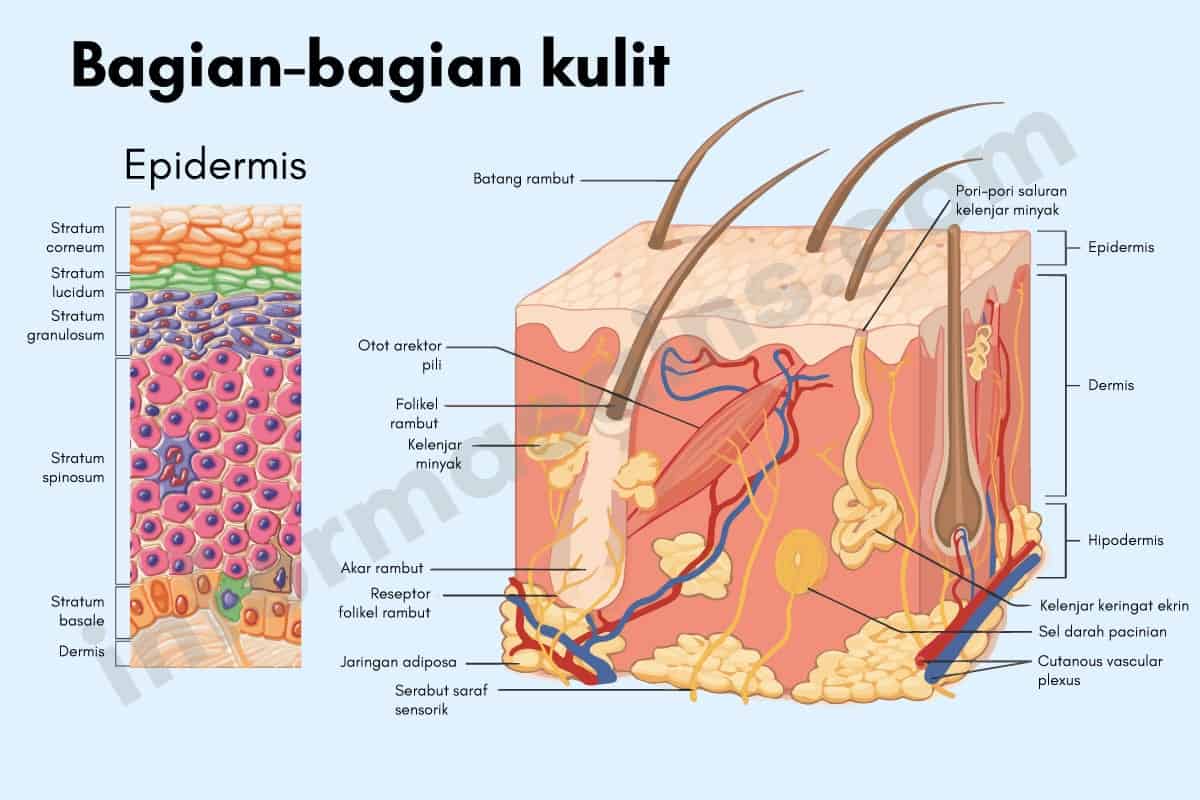
Hipodermis
In this study, small and wide angle X-ray diffraction were used to characterize the lipid organization in stratum corneum isolated from 14-day- old reconstructed epidermis. The measurements were carried out at room temperature, and subsequently as a function of tem- perature between 25°C and 109OC, followed by measurements after cooling to.

Stratum corneum anatomy, thickness, structure & stratum corneum function
The detailed ultrastructural, biochemical, and molecular dissection of the classic "bricks and mortar" model of the SC has provided insights into the basis of dry, scaly skin disorders that range from the cosmetic problems of winter xerosis to severe conditions such as psoriasis. ABSTRACT: Our understanding of the formation, structure, composition, and maturation of the stratum corneum (SC.

Lapisan kulit yang tidak mengandung pembuluh darah dan saraf adalah 2021
The ECM contains more than lipids. The title of the paper by Iwai et al. is somewhat misleading, because SC membrane domains are heterogeneous (Figure 1), containing not only lamellar bilayers but also the following: (1) corneocyte envelopes; (2) the ω-hydroxyceramide monolayer that surrounds corneocytes (i.e., the corneocyte lipid envelope); and (3) several other secreted enzymatic and.
Sistem Integumen
Recently advances in understanding the composition of this barrier have led to new insights into how it performs its roles and proposals of new therapies to improve healing in these circumstances. The stratum corneum is the outer most layer of mammalian skin. Its role is predominately as a barrier to protect an organism from external environmental insults and prevent excessive transcutaneous.

Structure of stratum corneum Royalty Free Vector Image
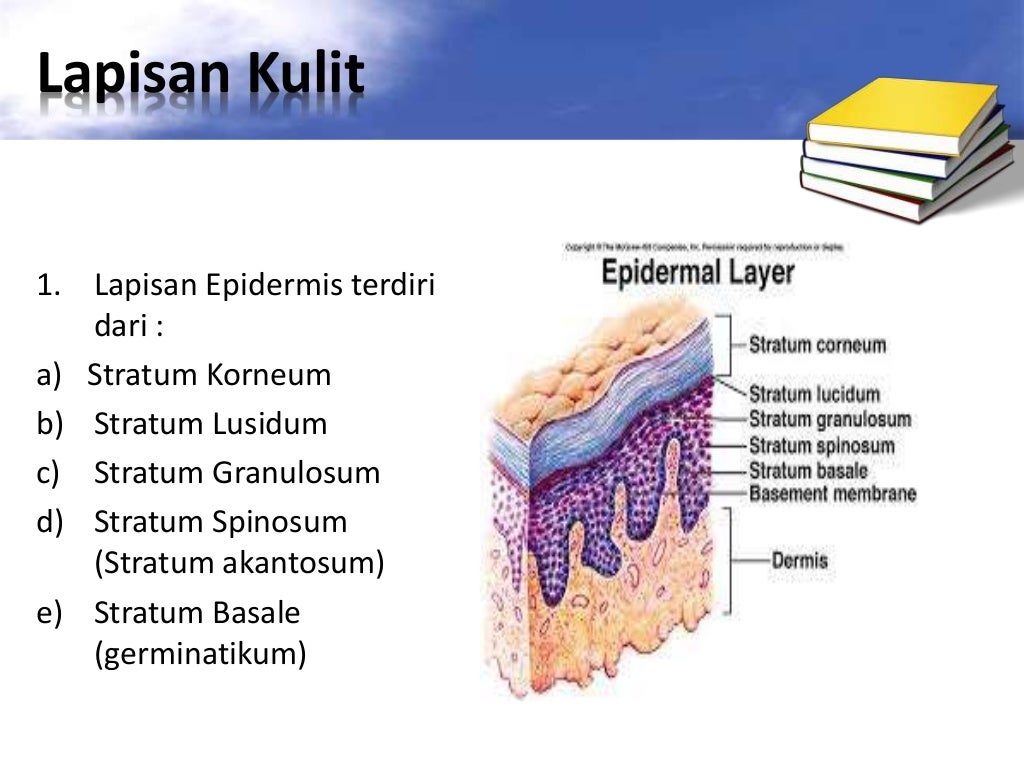
5 Bagian epidermis kulit tersusun atas lima lapisan kulit sebagai berikut : 1. Stratum Korneum Lapisan ini merupakan lapisan epidermis teratas yang terdiri dari sel-sel mati,

Anatomi Dan Fisiologi Kulit Skin anatomy, Integumentary system, Human anatomy and physiology
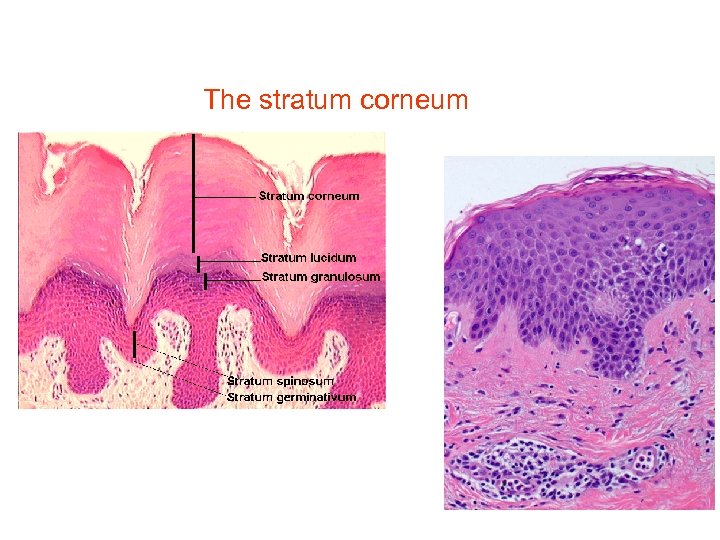
The human stratum corneum comprises 15 or so layers of flattened corneocytes and is divided into two layers: the stratum compactum and the stratum disjunctum. The stratum compactum is the deep, dense, cohesive layer, while the stratum disjunctum is looser and lies superficially to the stratum compactum. As the stratum disjunctum continues to.

The Stratum Corneum The Outermost Layer Of Epithelium Steve Gallik
1. Introduction. The particular functions of skin beyond its role as an interface are diverse and include thermal insulation and regulation [], defense against foreign pathogens [], touch-based sensation [], vitamin D production [], and prevention of water loss [5, 6].These roles are dependent on the skin's unique structure and composition, of which the epidermis serves as the outermost.

Anatomi Fisiologi Kulit pada Manusia
This chapter is divided in three parts as it explores stratum corneum biomechanics at three. different scales: the cellular level with descriptions of the corneocyte mechanical properties, the tissue level through mechanical properties obtained on in vitro stratum corneum layer, and. finally at the organ level through the description of the.

What is the Stratum Corneum? (with pictures)
The stratum corneum (SC) is the initial layer of the skin, with an average thickness of 20 to 30 μm, and the hardest substance to permeate for drug delivery consisting of several layers of.

Skin Cells and Structure Layers of epidermis. cornified (stratum corneum), clear or translucent
X-ray diffraction is one of the powerful tools in the study of a variety of structures in the stratum corneum at the molecular level. Resolving structural modifications during functioning is an important subject for clarifying the mechanism of operating principles in the function. Here, the X-ray diffraction experimental techniques used in the structural study on the stratum corneum are widely.
Stratum corneum How does your body keep
The crucial barrier properties of the stratum corneum (SC) depend critically on the design and integrity of its layered molecular structure. However, analysis methods capable of spatially resolved.

Stratum Corneum Diagram
As the outermost layer of the skin, the stratum corneum (SC) participates in the functional properties of the skin (1). It protects our body from harsh environmental factors and mechanical insults.

Diagrammatic representation of the stratum corneum and the... Download Scientific Diagram
Chapter 2 Stratum Corneum Yoshikazu Uchida and Kyungho Park Abstract The stratum corneum, consisting of denucleated keratinocytes, corneocytes that are eventually shed from skin, is a highly-functional outer layer

Describing normal and healthy stratum corneum layer of skin with... Download Scientific Diagram
The stratum corneum has an elegantly simple two-compartment structural organization at the light microscopic level, with the corneocytes embedded in a lipid matrix, as visualized by frozen sections, swollen in alkaline buffer and stained with a dye (Christophers and Kligman, 1964), or when stained with Nile red, a fluorescent lipid stain (Simonetti et al., 1995).

Structure of epidermis cornified (stratum corneum), clear or translucent layer (lucidum
Schematic representation of (a) the layers in the epidermis. Stratum corneum, the topmost layer of epidermis, contains rigid corneocytes. (b) Lipid matrix between corneocytes show lamellar structure.

Stratum corneum anatomy, thickness, structure & stratum corneum function
The stratum corneum (SC), the skin's outermost layer and interface with the outside world is now well recognized as the barrier that prevents unwanted materials from entering, and excessive loss of water from exiting the body. This review summarizes the major advances in our understanding of this formidable membrane.