Fracturas de Le Fort Concise Medical Knowledge
Fratura Le Fort 1 por Trauma CIRURGIA
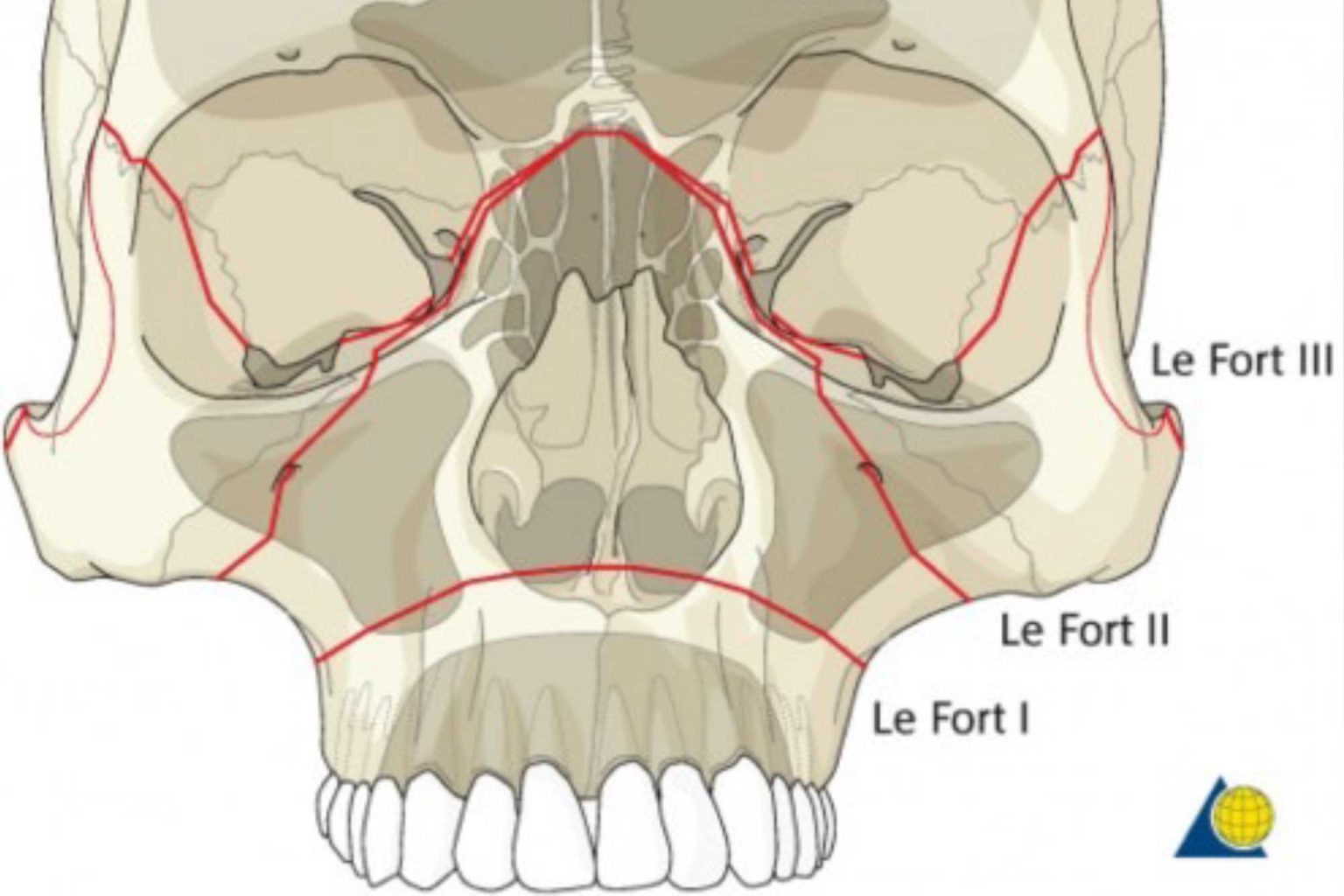
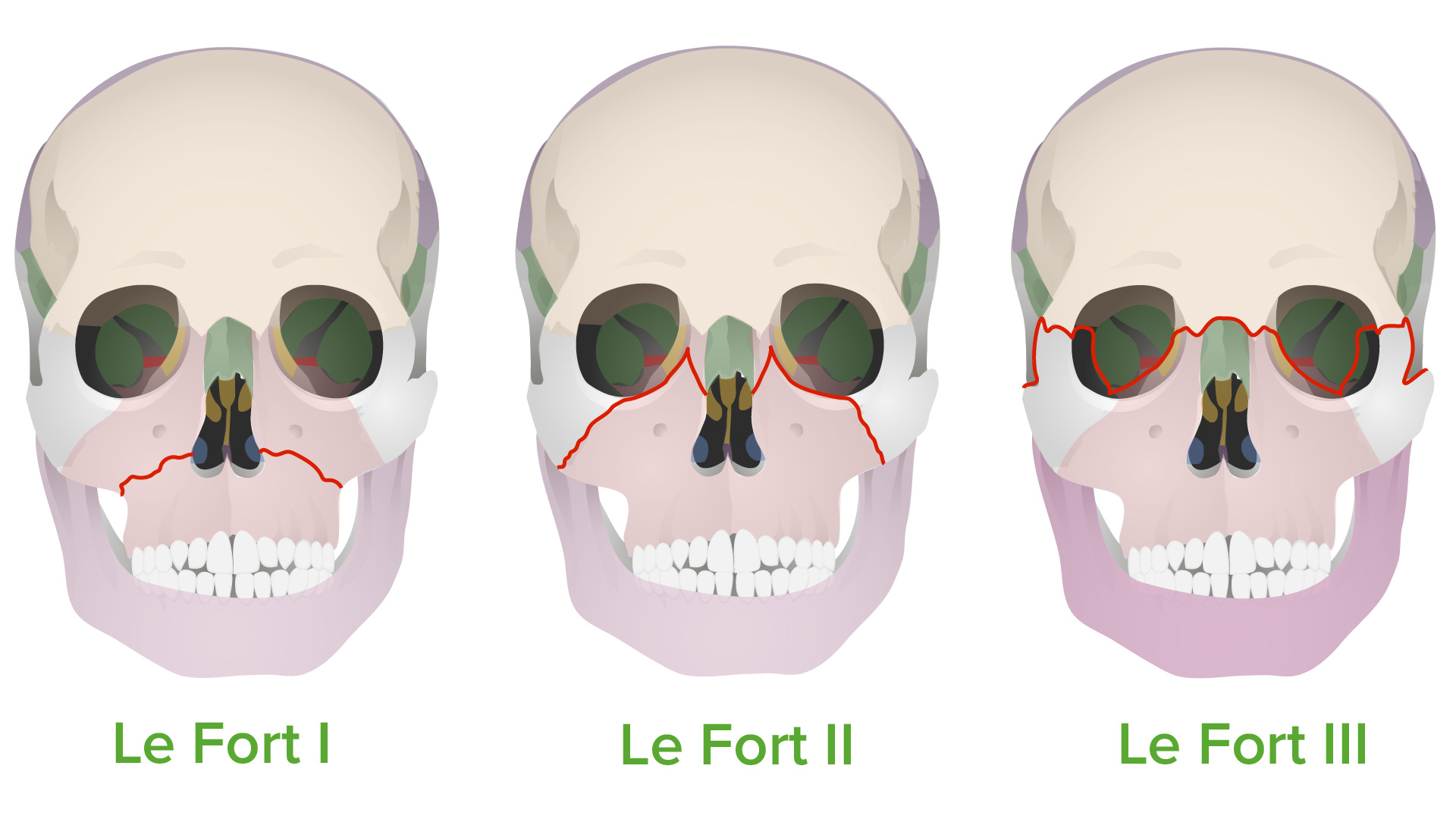
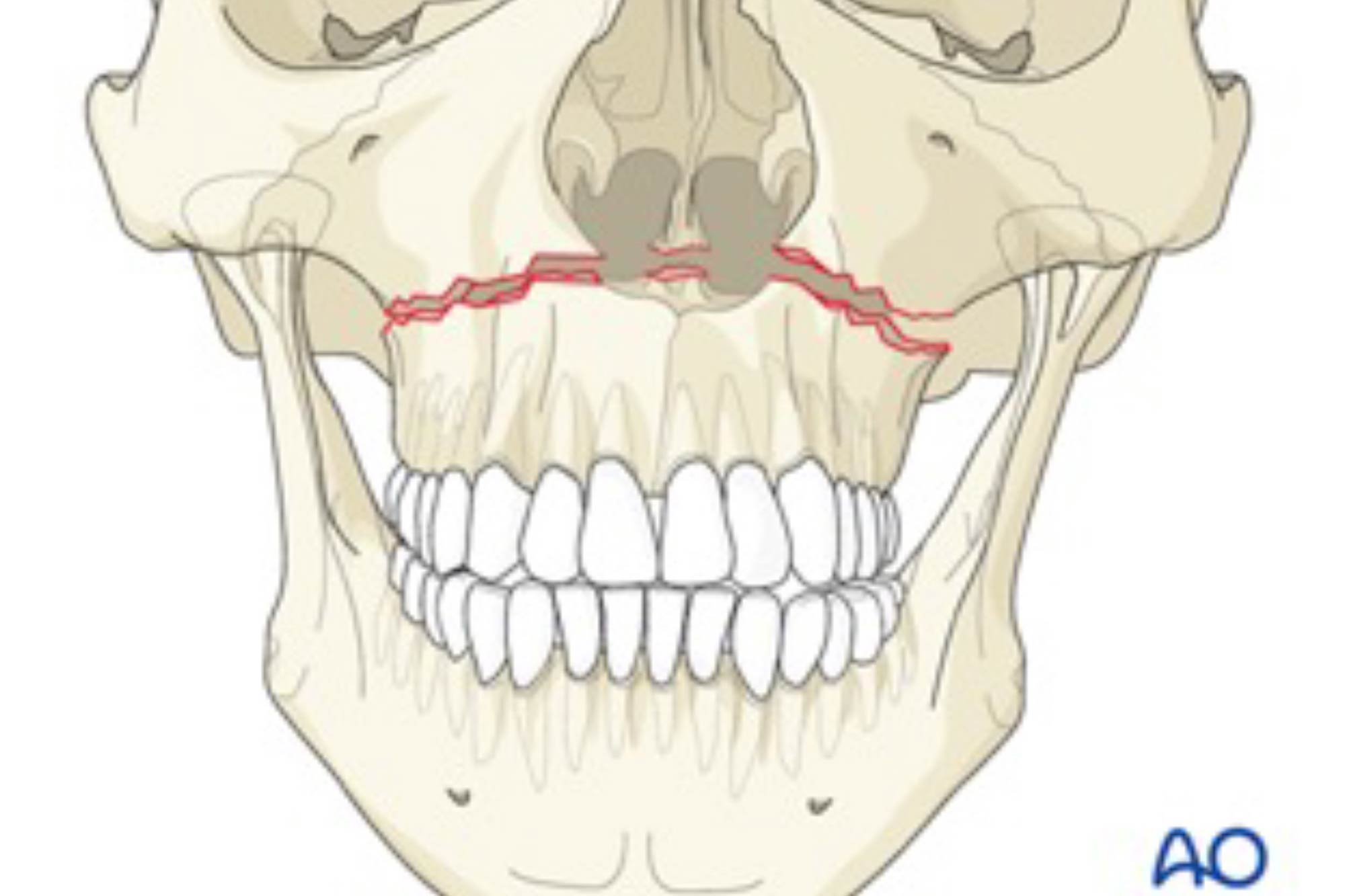
Le Fort I level fractures are essentially a separation of the hard palate from the upper maxilla due to a transverse fracture running through the maxilla and pterygoid plates at a level just above the floor of the nose. LeFort II fractures transect the nasal bones, medial-anterior orbital walls, orbital floor, inferior orbital rims and finally.

Facial Fractures, Emergency Medicine Diseases & Conditions 5MinuteConsult
The Le Fort fractures are a pattern of midface fractures originally described by the French surgeon, René Le Fort, in the early 1900s. [1] Le Fort studied the effect of facial trauma by dropping cadavers from various heights and recording the different fracture patterns observed. [2] Today, with the evolution of high-speed motor vehicle.
A Dental Student's Guide to...Le Fort fractures Dentistry
Introduction. Initially described in 1901 by French surgeon René Le Fort (1869-1951), LeFort fractures represent a group of midface fractures that occur following blunt trauma and follow areas of structural weakness. Common etiologies include assault, facial trauma in contact sports, motor vehicle accidents (MVA), or falls from significant.

LeFort Klassifikation Ars Neurochirurgica
Le Fort Type II: "Floating maxilla". This fracture involves extension of the fracture superiorally. Includes fractures of the nasal bridge, maxilla, lacrimal bones, and orbital floors and rims. Typically bilateral and triangular in shape. Le Fort Type III: "Floating face". Rare but are considered "craniofacial dysjunction".
Fracturas de Le Fort Concise Medical Knowledge
Introduction. Originally described by Rene Le Fort in 1901, Le Fort fractures are specific facial bone fracture patterns that occur in the setting of blunt facial trauma (most commonly involving motor vehicle collision, assault, or falls) [1,2].All Le Fort fracture types involve the pterygoid processes of the sphenoid bones and therefore, disrupt the intrinsic buttress system to the midface.

Le Fort Fracture Definition Fracture Types And Symptoms My XXX Hot Girl
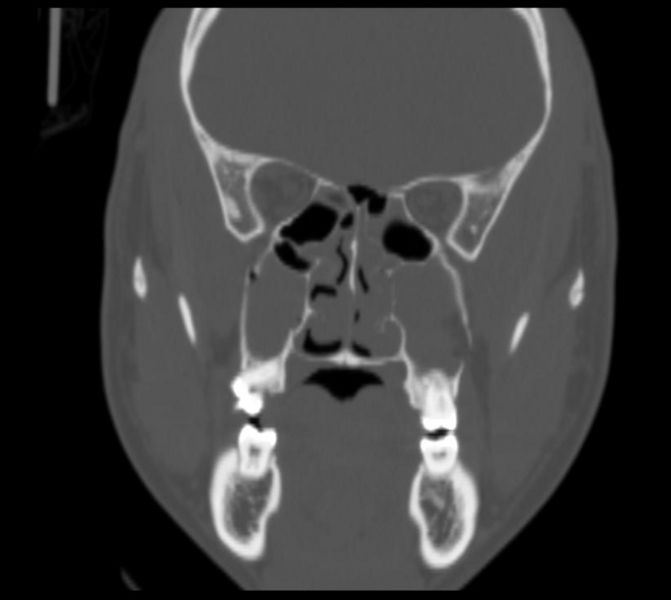
The nasal dorsum was flattened. These findings were consistent with the CT findings of bilateral Le Fort I fractures and nasoseptal fractures. A nasal septal hematoma was ruled out by a speculum exam. The nasal laceration was repaired at the bedside. The maxillofacial fractures were operatively treated on a non-emergency basis.
Le Fort Fractures (LFF) are fractures of the mid face. GrepMed
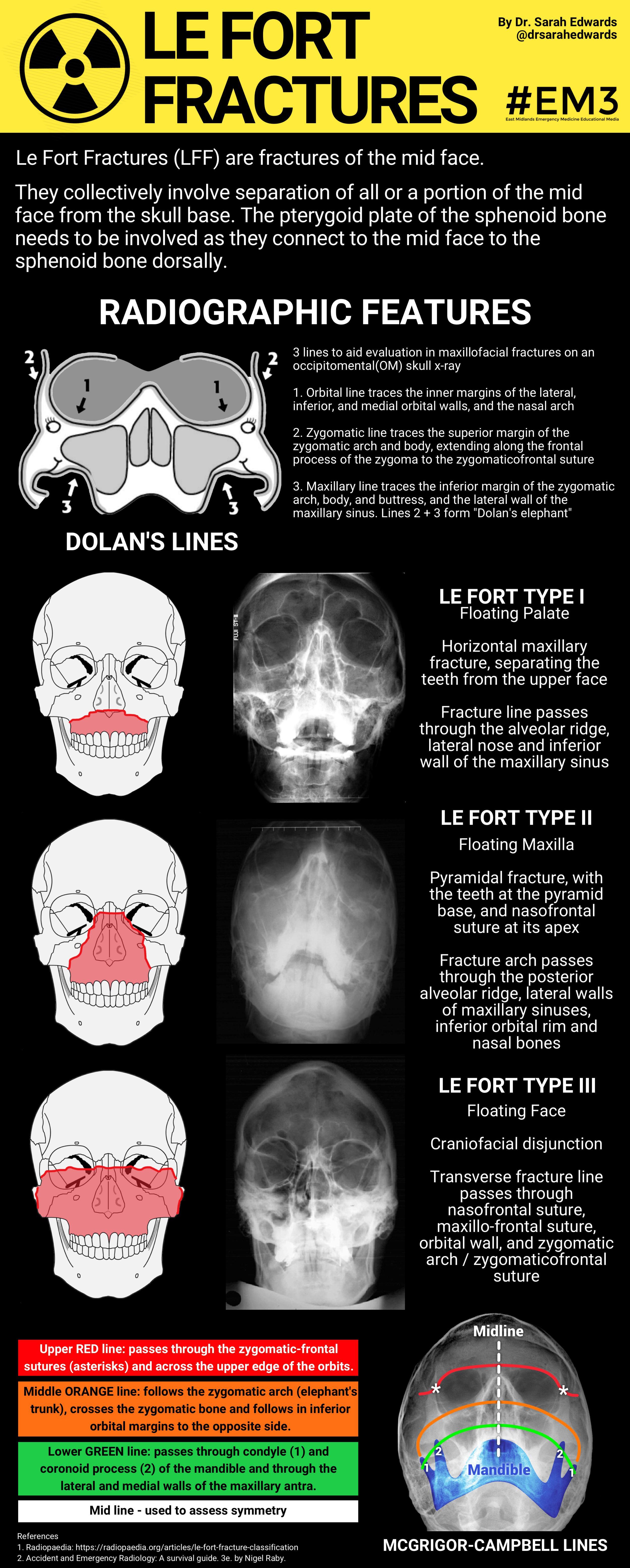
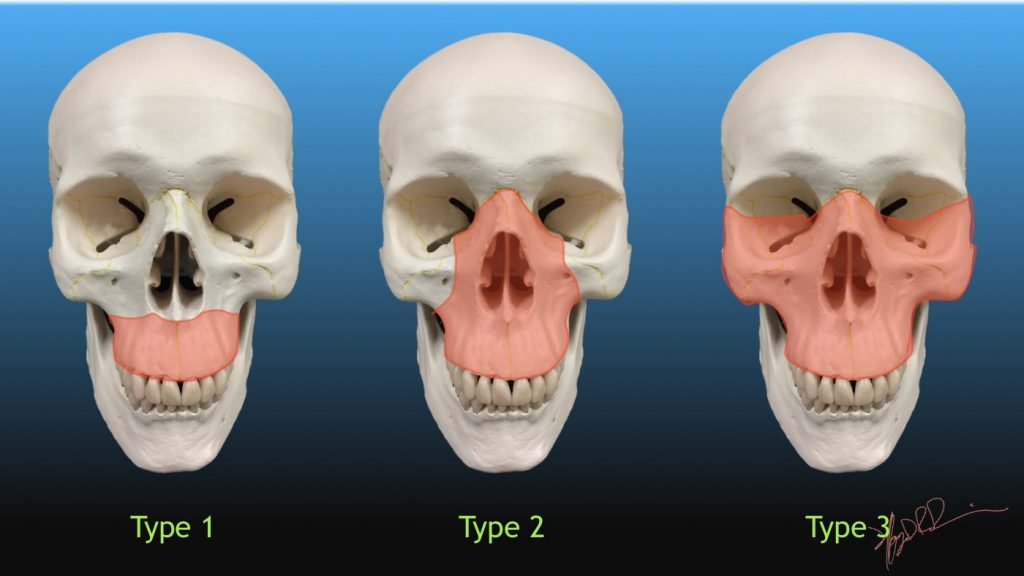
Le fort fracture classification : Type 1 - Fracture line passes through the alveolar ridge, lateral nose and inferior wall of the maxillary sinus. Type 2 - Fracture arch passes through the posterior alveolar ridge , lateral walls of maxillary sinuses, inferior orbital rim and nasal bones. Type 3 - Transverse fracture line passes through the.

Radiology MRI Le Fort Type 1 Fracture
History of Le Fort Fractures. In 1901, René Le Fort published his experimental findings of facial fracture patterns. His studies involved subjecting cadaver skulls to various forces of impact and analyzing the fractures that resulted. He described that fractures tended to occur in characteristic locations, which he noted corresponded to.
Radiology (kawasan radiasi) Fraktur Cruris Pada TibiaFibula
Le Fort I fractures may be accessed by a gingivobuccal sulcus incision, and fixed by reestablishing the midfacial buttresses using 1.5 to 2.0 mm L and J plates. To prevent the forces of mastication from disrupting the repair, emphasis must be put on placing the plates in the same direction as the forces of mastication [ 6 ].

Le Fort Fractures Core EM
The LeFort I osteotomy is a horizontal maxillary osteotomy utilized in the correction of midface deformities allowing movement anteriorly/posteriorly, vertically, rotationally, and with segmentation: expansion. It can also be utilized to facilitate surgical access for the removal of tumors or the reduction of complex midfacial fractures. It is named in accordance with the LeFort I horizontal.
LeFort Classification of Facial Fractures UW Emergency Radiology
Learn the Le Fort fracture types and classification system mnemonic: Le Fort type I (1), Le Fort type II (2), and Le Fort type III (3) facial fractures. Remember Le Fort fracture types using see no evil, hear no evil, speak no evil. Learn what facial bones are involved on radiology including the max
LeFort fracture wikidoc
Le Fort I is a floating palate (horizontal) Le Fort II is a floating maxilla (pyramidal) Le Fort III is a floating face (transverse) Any combination is possible. For example, there may be type 2 on one side and contralateral type 3, or there may be unilateral type 1 and 2 fractures. It should be noted that Le Fort fractures are often associated.

Lefort 1 Fracture
This diagram demonstrates the pattern of a bilateral Le Fort 1 fracture. 1 article features images from this case. Le Fort fracture classification; 10 public playlists include this case. Trauma by Grace; Neurotrauma by Gregorius Enrico, dr., Sp.Rad, MARS; ANZCA.

Le Fort 1 Down Fracture YouTube
Le Fort injuries are complex fractures of the midface, named after Rene Le Fort who studied cadaver skulls that were subjected to blunt force trauma. His experiments determined the areas of structural weakness of the maxilla designated as "lines of weakness" where fractures occurred. These fractures are classified into 3 distinct groups based on the direction of the fracture: horizontal.
A Dental Student's Guide to...Le Fort fractures Dentistry
Le Fort fractures are typically the result of forceful impact to the face. They are often caused by rapid deceleration car crashes in which the midface strikes a stationary object, such as the car's dashboard. It can also occur if the midface is struck by a rigid object, such as a baseball bat. If the force is directed at the midface straight.

Le Fort 1 Pterygoid Plate Separation YouTube
Patient Data. Left zygomaticomaxillary complex fracture: Fracture of the lateral orbital rim, zygomatic arch, inferior orbital rim and anterior and posterior maxillary sinus walls. Right maxillary horizontal fracture separating the teeth from the upper face (Le Fort type 1). No significant hematosinus. Note is made for peripheral mucoperiosteal.