Stoichiometry Chemistry Activities
PPT Chapter 12 Stoichiometry PowerPoint Presentation, free download
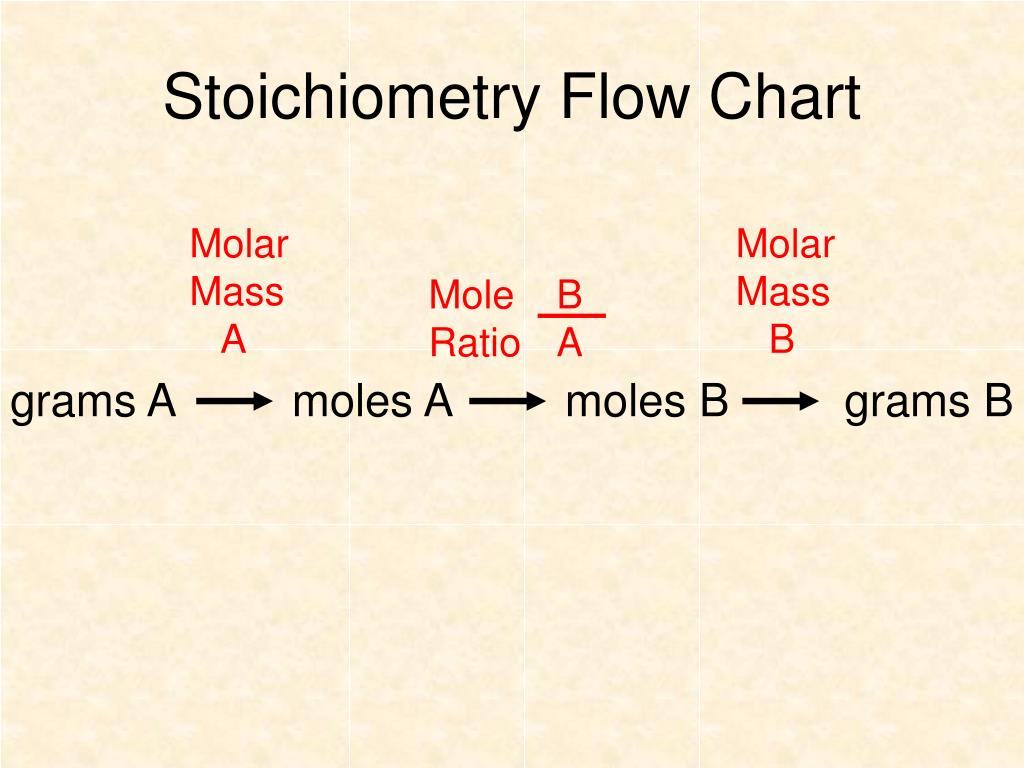
Stoichiometry Flow Chart Laura Zimny 555 subscribers Share Save 540 views 2 years ago Covers the steps of basic conversions within stoichiometry without using dimensional analysis. Show more.
Stoichiometry of Reactions in Solution
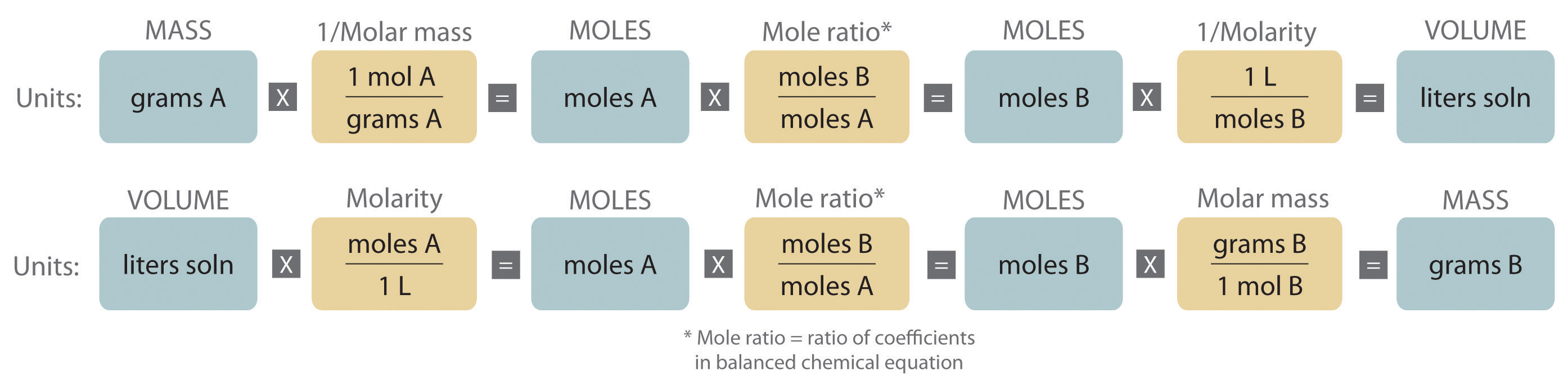
The flow chart depicts the various computational steps involved in most reaction stoichiometry calculations. Airbags. Figure 3. Airbags deploy upon impact to minimize serious injuries to passengers.. A balanced chemical equation may be used to describe a reaction's stoichiometry (the relationships between amounts of reactants and products.
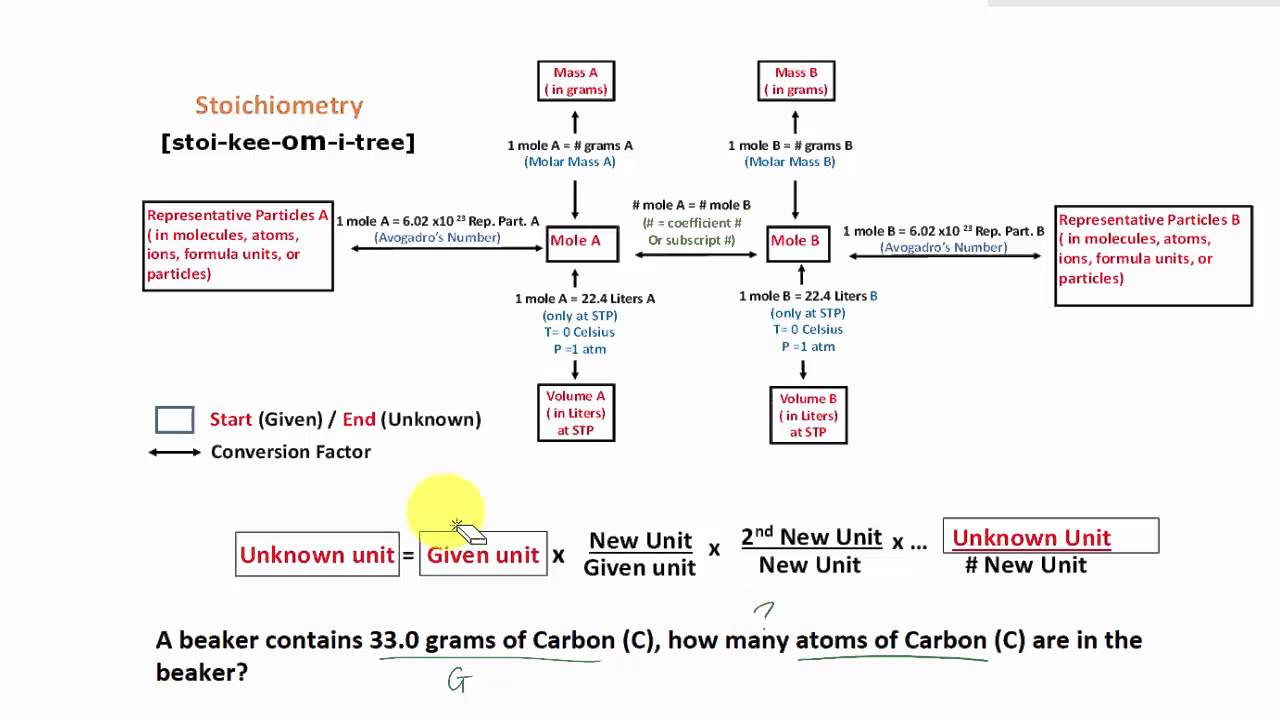
stoichiometry flowchart introduction YouTube
The stoichiometry of a balanced chemical equation identifies the maximum amount of product that can be obtained. The stoichiometry of a reaction describes the relative amounts of reactants and products in a balanced chemical equation. A stoichiometric quantity of a reactant is the amount necessary to react completely with the other reactant (s).
Stoichiometry Chemistry Activities
4 Chapter 3: Stoichiometry Limiting Reagents and Theoretical Yields Limiting Reagent: The reactant that governs the maximum amount of product that can form. Identifying The Limiting Reagent Step 1: Calculate the amount of each reactant in moles. Step 2: Choose one of the reactants and use the mole ratio to calculate the theoretical amount

Flow chart for Stoichiometry classroom Pinterest
Stoichiometry, Flow Chart, Moles to Mass Conversion

Chapter 11 Mr. Burkett's Science Classroom
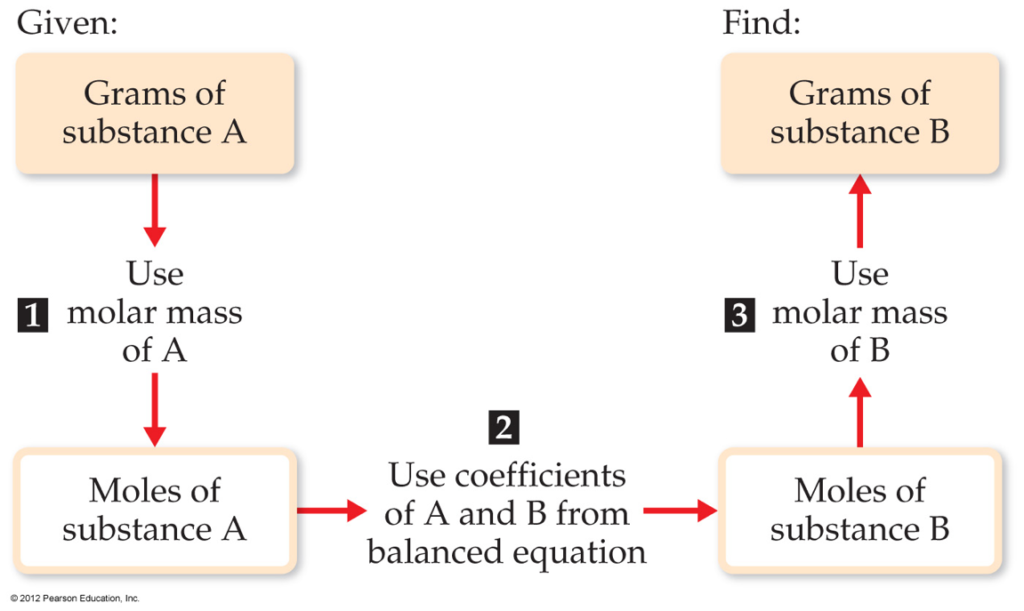
Flowchart of steps in stoichiometric calculations. Step 1: grams of A is converted to moles by multiplying by the inverse of the molar mass. Step 2: moles of A is converted to moles of B by multiplying by the molar ratio. Step 3: moles of B is converted to grams of B by the molar mass.

Stoichiometry Flow Chart YouTube
These stoichiometric factors can be used to compute the number of ammonia molecules produced from a given number of hydrogen molecules, or the number of hydrogen molecules required to produce a given number of ammonia molecules. Similar factors may be derived for any pair of substances in any chemical equation.

Stoichiometric Calculations CK12 Foundation
A common type of stoichiometric relationship is the mole ratio, which relates the amounts in moles of any two substances in a chemical reaction. We can write a mole ratio for a pair of substances by looking at the coefficients in front of each species in the balanced chemical equation.

Pin on Chemistry woes
Reaction Flow Chart Reaction Table Beautiful Chemical Reactions(Vimeo) Chapter 6 Stoichiometry: Lecture:6ab, 6 c, 6 d, Homework: 6a , 6b , 6c , 6d Extra Practice: EP 1, EP 1 - Answer key Study Guide: SG - 9: Simple Conversions Harder Conversions Titration Problems: Read (6a-d): Lumen - Stoichiometry Stoichiometry Flow Chart: Exam 3
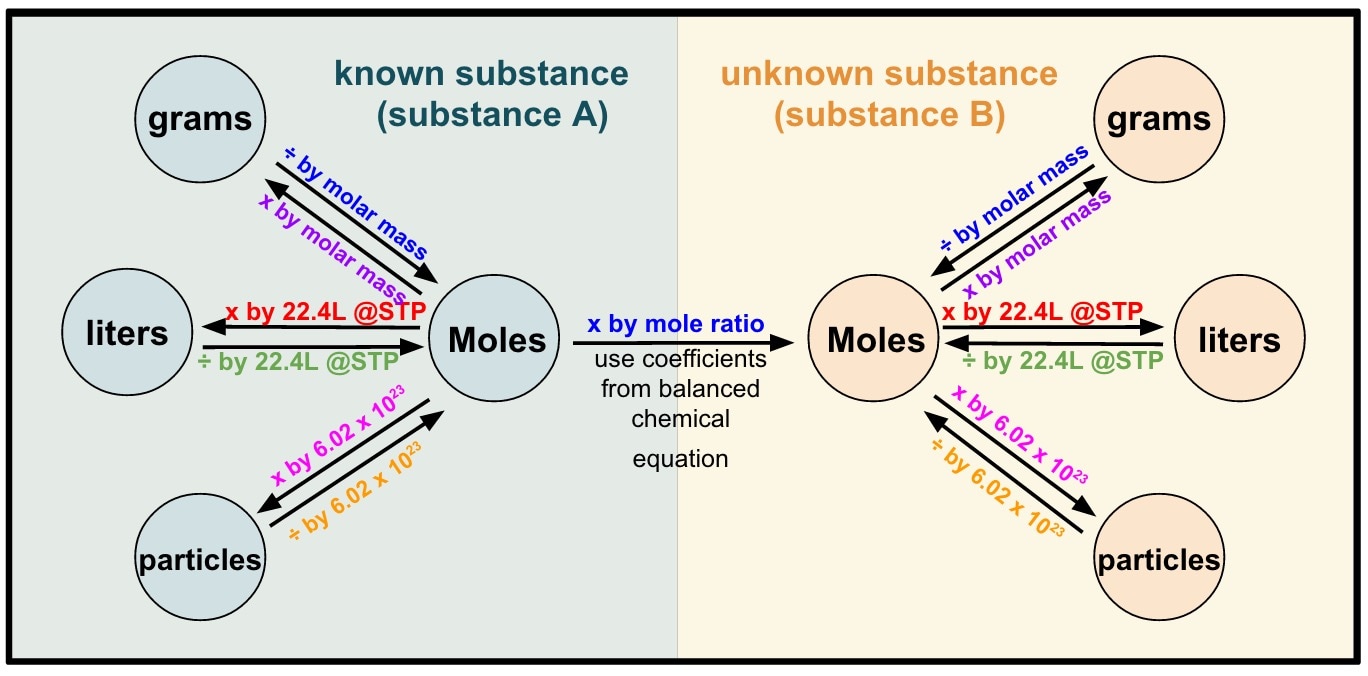
Stoichiometry Review Mr. Siemianowski Eisenhower High School
Stoichiometry Flow Chart The Mathematics of Chemical (Stoichiometry) major task of the chemist is to project how much product produced must have more value than the reactants The cost of the energy used in the reaction or the cost consideration. A chemical engineer must be able to process is economical. stoichiometry.

Stoichiometry Chart YouTube
Stoichiometry of Chemical Reactions Figure 4.1 Many modern rocket fuels are solid mixtures of substances combined in carefully measured amounts and ignited to yield a thrust-generating chemical reaction. (credit: modification of work by NASA) Chapter Outline 4.1Writing and Balancing Chemical Equations 4.2Classifying Chemical Reactions
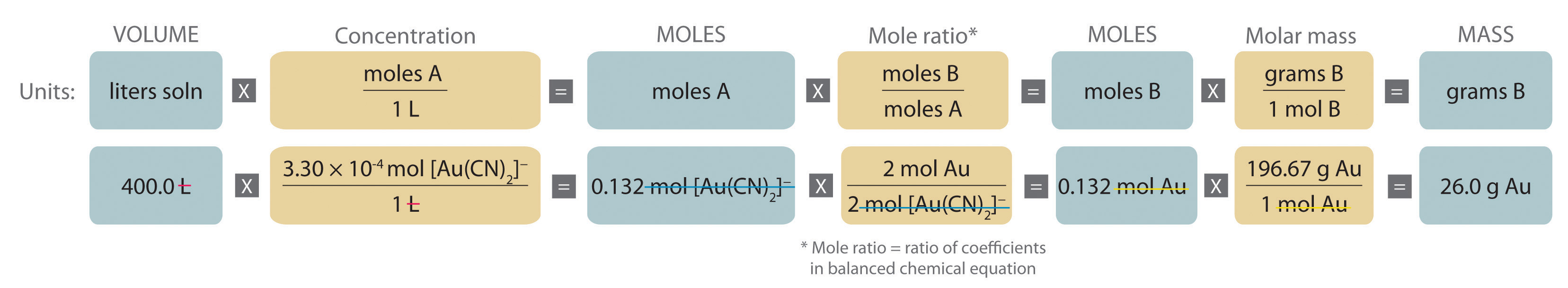
Stoichiometry of Reactions in Solution
Stoichiometry ( / ˌstɔɪkiˈɒmɪtri /) is the relationship between the weights of reactants and products before, during, and following chemical reactions .
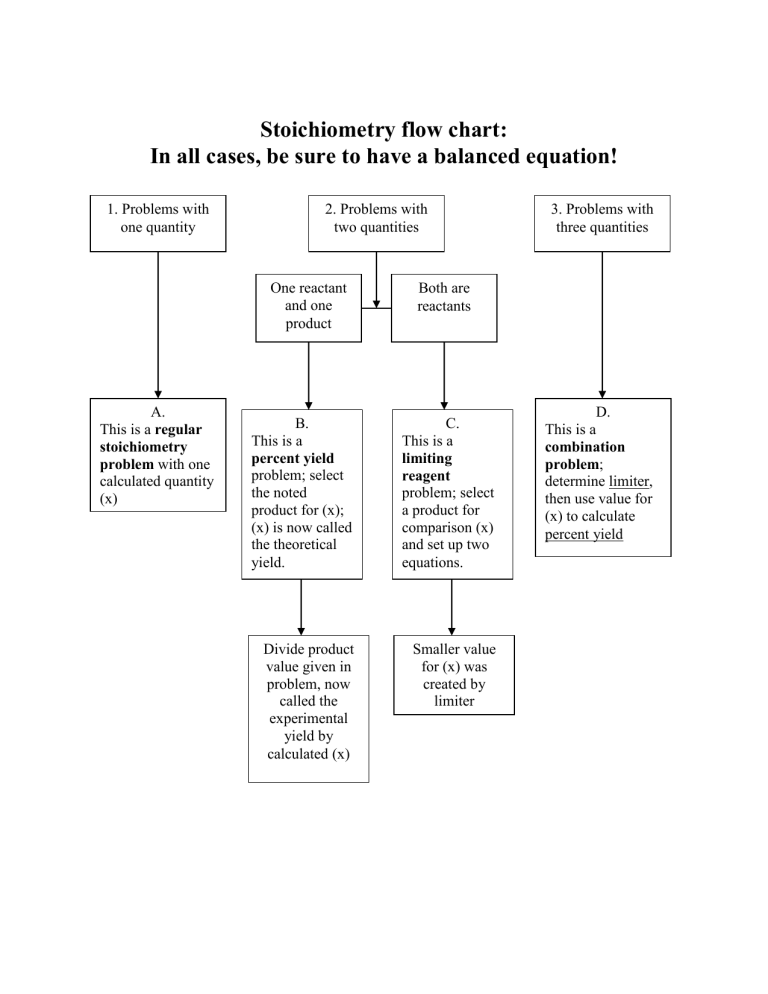
Stoichiometry flow chart
CHAPTER 3 STOICHIOMETRY OF FORMULAS AND EQUATIONS 3.1 Cl 35.45 amu ≡ 35.45 g/mol Cl Mass Cl = (3 mol Cl) x (35.45 g Cl/l mol Cl) = 106.4 g Cl Al 26.98 amu ≡ 26.98 g/mol Al Mass Al = (2 mol Al) x (26.98 g Al/l mol Al) = 53.96 g Al 3.2 Plan: The formulas are based on the mole ratios of the constituents. Avogadro's number allows the change from

Ms J's Chemistry Class 10/01/2017 11/01/2017
Anatomy of a Chemical Equation CH4 (g) + 2 O2 (g) CO2 (g) + 2 H2O (g) Coefficients are inserted to balance the equation. Subscripts and Coefficients Give Different Information • Subscripts tell the number of atoms of each element in a molecule Subscripts and Coefficients Give Different Information

Reaction Stoichiometry CHEM 1305 Introductory Chemistry
One can find the percentage of the mass of a compound that comes from each of the elements in the compound by using this equation: (number of atoms)(atomic weight) % element = (FW of the compound) x 100. Percent Composition. So the percentage of carbon in ethane is. (2)(12.0 amu) %C = (30.0 amu) = 24.0 amu. 30.0 amu.
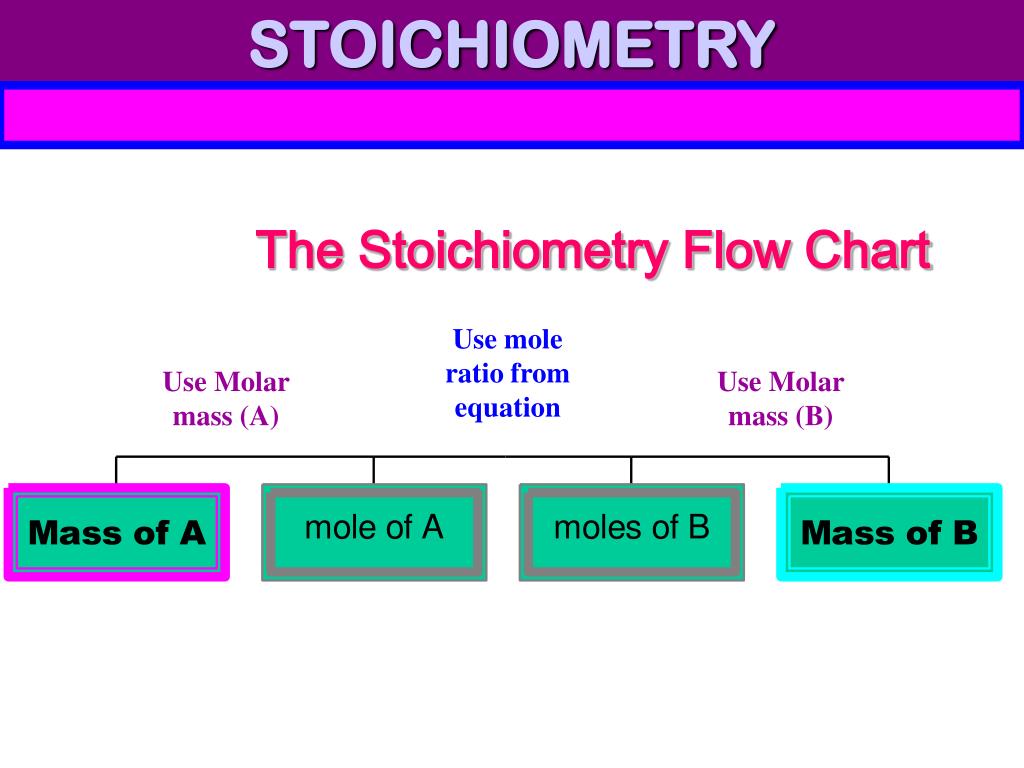
PPT STOICHIOMETRY PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID4499255
CHM 130 Stoichiometry Worksheet. The following flow chart may help you work stoichiometry problems. Remember to pay careful attention to what you are given, and what you are trying to find. Fermentation is a complex chemical process of making wine by converting glucose into ethanol and carbon dioxide: C 6 H 12 O 6 (s) 2 C 2 H 5 OH (l) + 2 CO 2 (g)