Neuron Diagram Straight from a Scientist
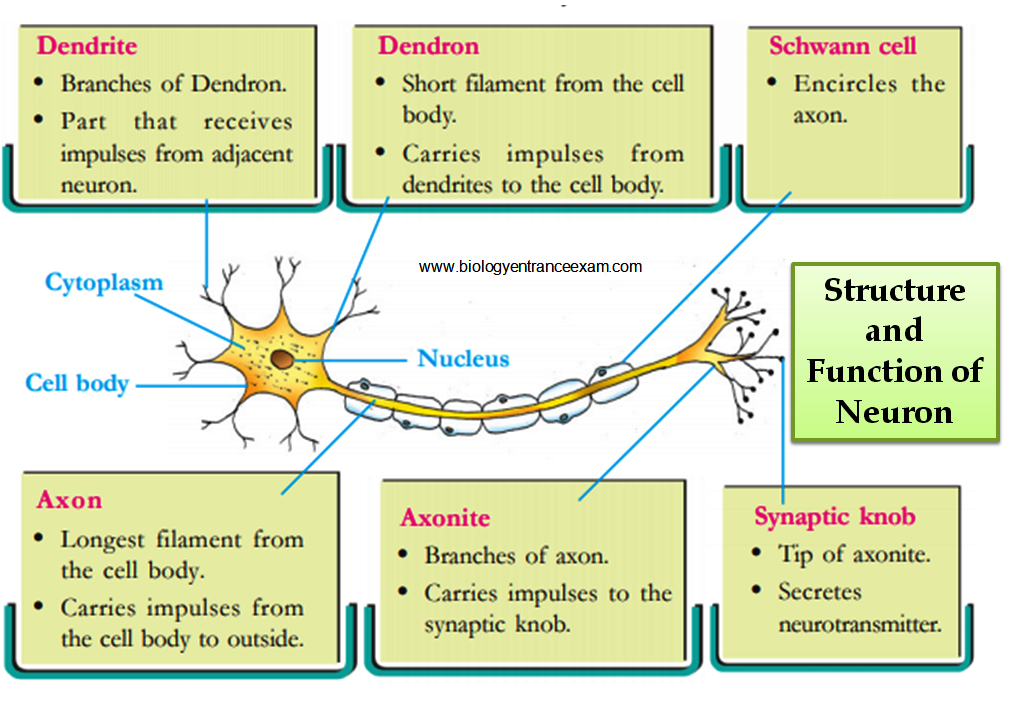
Structure and Function of Neuron
Diagram Of Neuron. A neuron is a specialized cell, primarily involved in transmitting information through electrical and chemical signals. They are found in the brain, spinal cord and the peripheral nerves. A neuron is also known as the nerve cell. The structure of a neuron varies with their shape and size and it mainly depends upon their.

Labeled Neuron Diagram Synapse Jasminea level
3. How to Draw a Neuron Diagram To learn about the structure of the neurons, the students can use a neuron labeled diagram. The students may follow these steps to make their neuron diagram, but the process is complex: 3.1 How to Draw a Neuron Diagram from Sketch Step 1: First, the students need to draw a circle. Based on it, they need to draw a.

related keywords suggestions for neurons structure and Neuronas, Khan
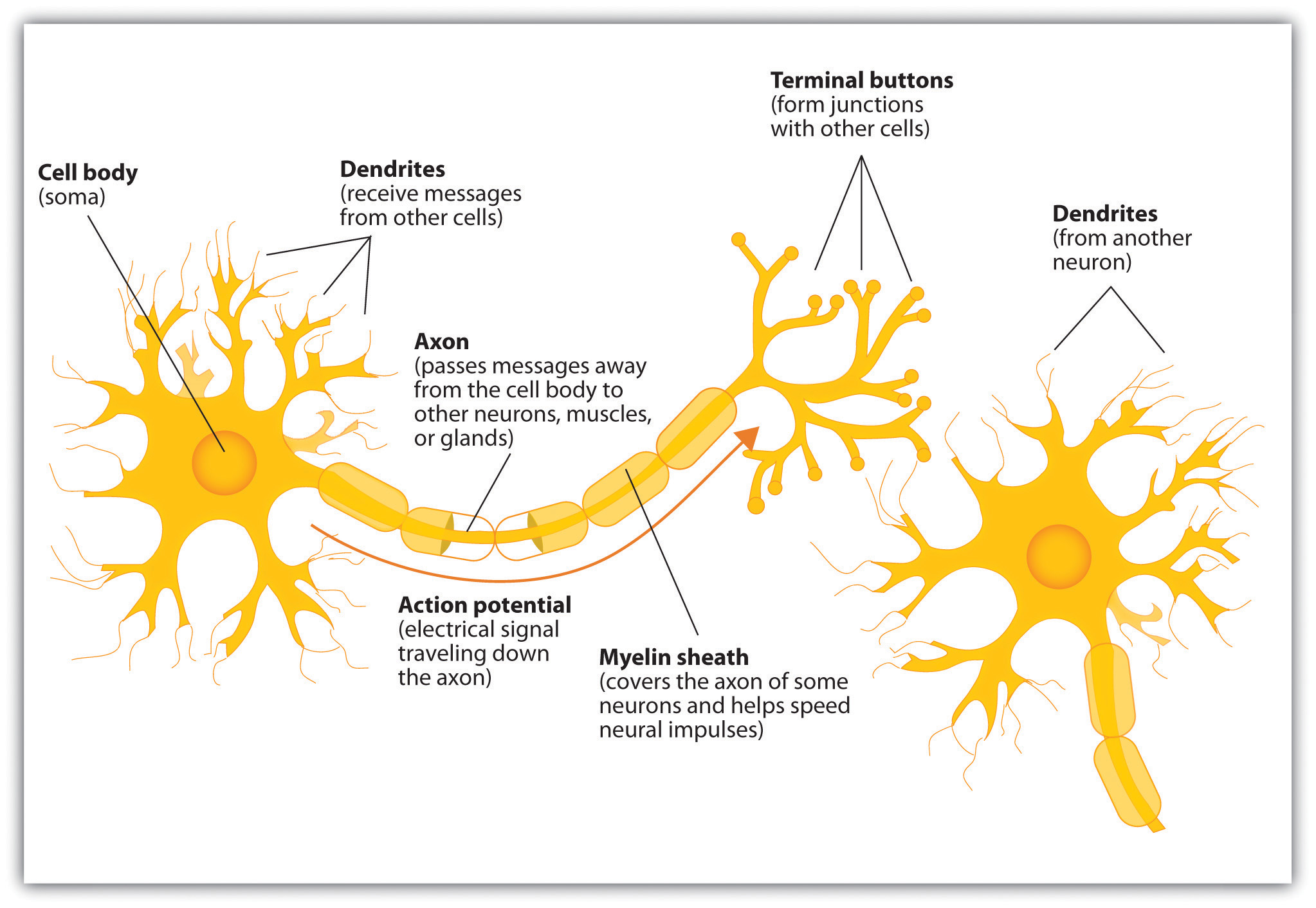
Neuron Anatomy. Nerve Cell: Dendrites receive messages from other neurons. The message then moves through the axon to the other end of the neuron, then to the tips of the axon and then into the space between neurons. From there the message can move to the next neuron. Neurons pass messages to each other using a special type of electrical signal.
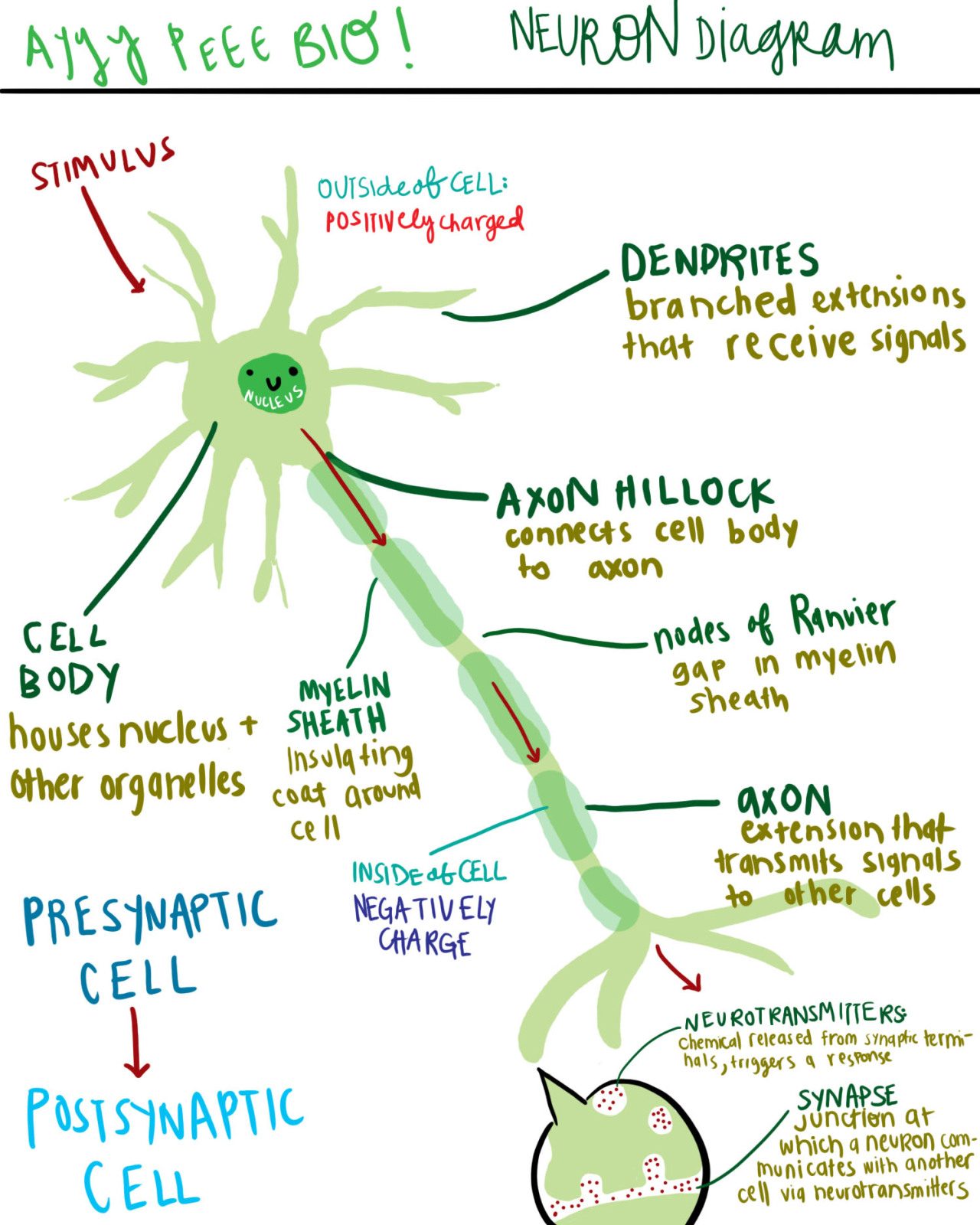
A diagram of a neuron and its functions. a study in chartreuse
Simplified diagram of neural circuits involved in the knee-jerk reflex. When the patellar tendon is tapped, the quadriceps muscle on the front of the thigh is stretched, activating a sensory neuron that wraps around a muscle cell. The sensory neuron's axon extends all the way into the spinal cord, where it synapses on two targets:

Neurons What are they and how do they work?
While they have the common features of a typical cell, they are structurally and functionally unique from other cells in many ways. All neurons have three main parts: 1) dendrites , 2) cell body or soma, and 3) axons. Besides the three major parts, there is the presence of axon terminal and synapse at the end of the neuron.
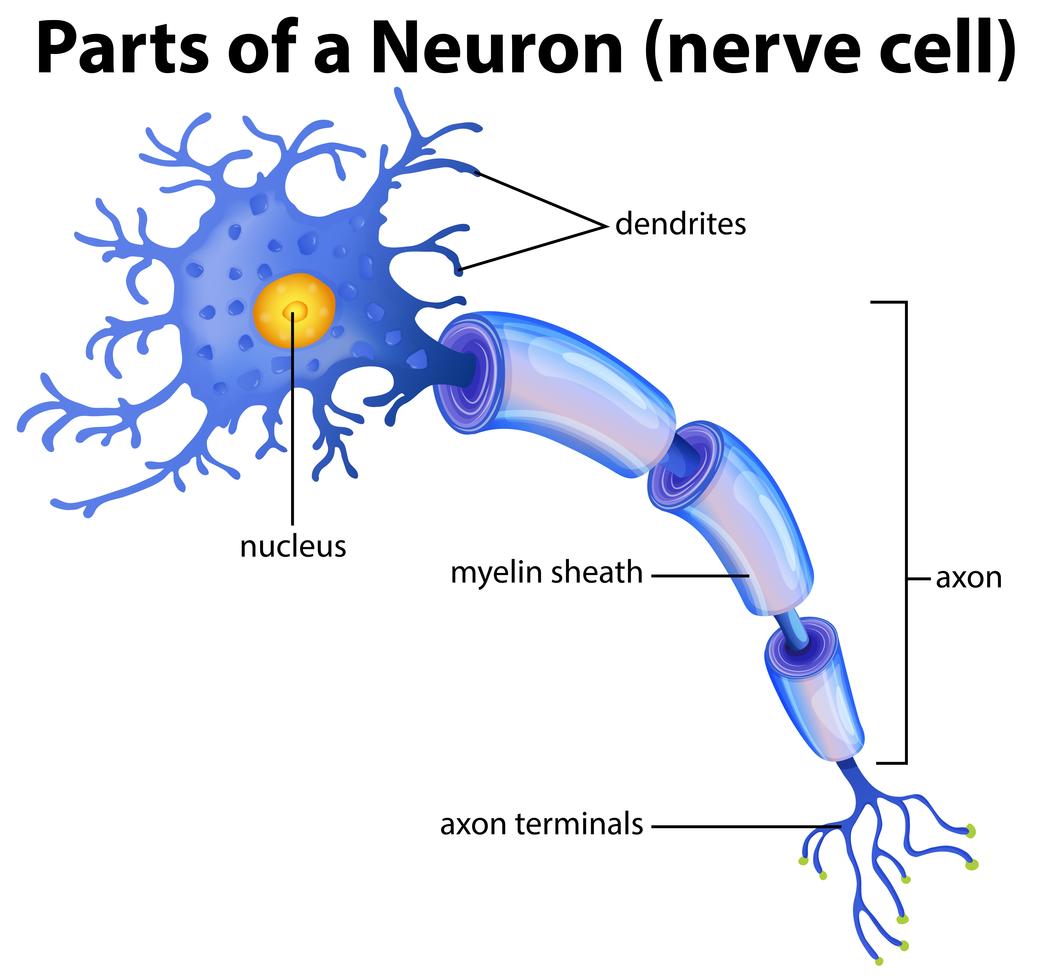
Part of a Neuron Diagram 299698 Vector Art at Vecteezy
Choose the correct names for the parts of the neuron. (6) This neuron part receives messages from other neurons. (7) This neuron part sends on messages to other neurons. (8) This neuron part gives messages to muscle tissue. (9) This neuron part processes incoming messages. (10) This neuron part contains instructions for making proteins that the.
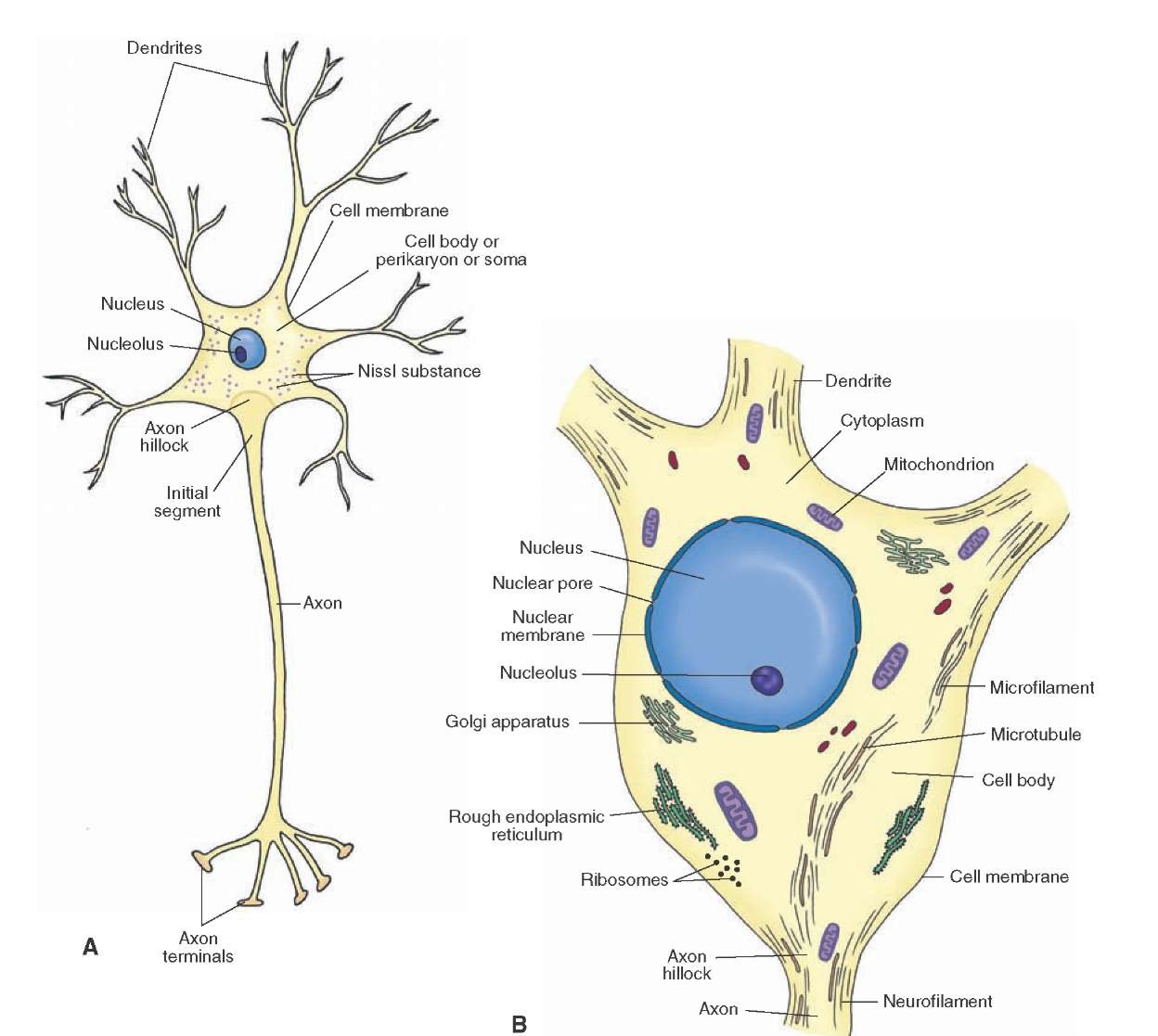
Histology of the Nervous System (The Neuron) Part 1
Throughout this article, you got the different neurons labelled diagrams. Here, you will also find the diagrams of different neuron types under a microscope. The neuron diagram shows the different parts (axon, dendrites, and cell body) of the neurons. You may also find more neuron diagrams on social media of anatomy learners.

Draw A Neuron And Label Its Parts Q10 A Draw The Structure Of Neuron
Neurotransmitters. The chemical signals that neurons use to communicate with other neurons and cells. It is the chemical involved in impulse transmission. Neuron transportation. Neurons generally transport signals in one direction from the dendrites, through the soma, along the axon and unto the terminal buttons. Term.
The Neuron Is the Building Block of the Nervous System USE ME
An Easy Guide to Neuron Anatomy with Diagrams. Neurons, also known as nerve cells, send and receive signals from your brain. While neurons have a lot in common with other types of cells, they're.
Explainer What is a neuron? Science News for Students
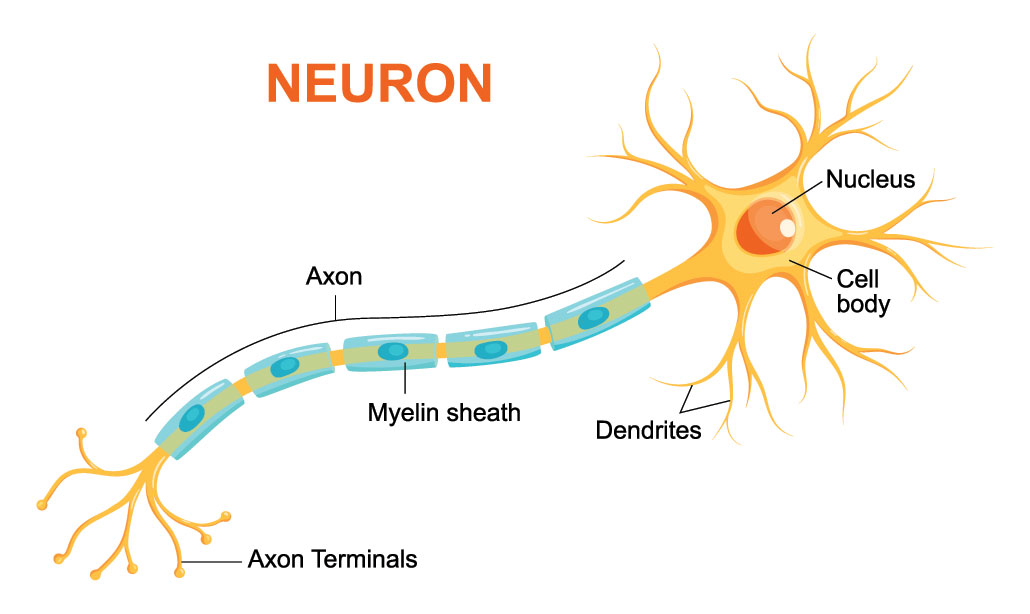
Complete neuron cell diagram. Neurons (also known as neurones and nerve cells) are electrically excitable cells in the nervous system that process and transmit information. In vertebrate animals, neurons are the core components of the brain, spinal cord and peripheral nerves. embedded text that can be translated into your language, using any.
What Is the Connection between Stress and the Nervous System?
Anatomy and histology Diagram of the components of a neuron. Neurons are highly specialized for the processing and transmission of cellular signals. Given their diversity of functions performed in different parts of the nervous system, there is a wide variety in their shape, size, and electrochemical properties.

FileNeuron1.jpg Wikimedia Commons
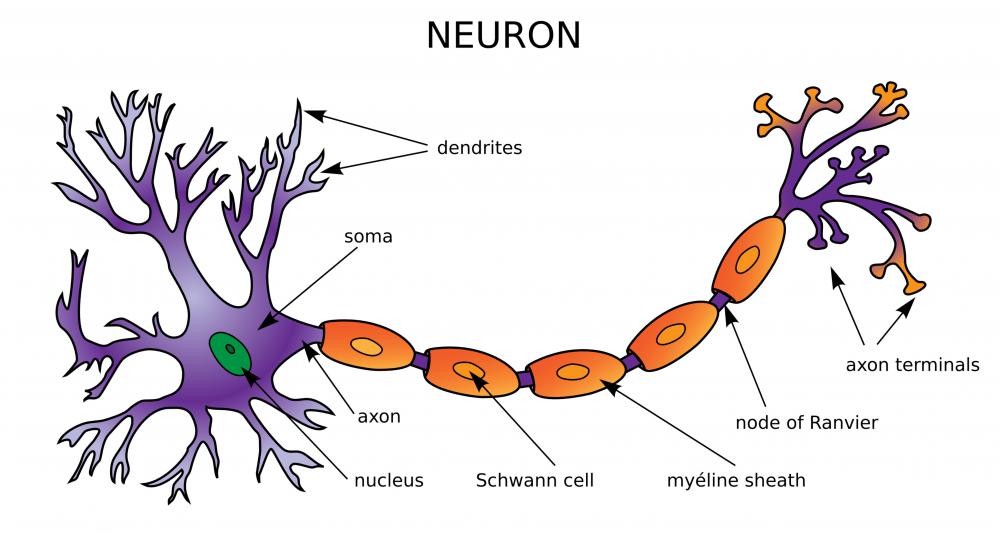
neuron, basic cell of the nervous system in vertebrates and most invertebrates from the level of the cnidarians (e.g., corals, jellyfish) upward.A typical neuron has a cell body containing a nucleus and two or more long fibres. Impulses are carried along one or more of these fibres, called dendrites, to the cell body; in higher nervous systems, only one fibre, the axon, carries the impulse.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/neuron-anatomy-58530ffe3df78ce2c34a7350.jpg)
Neuron Anatomy, Nerve Impulses, and Classifications
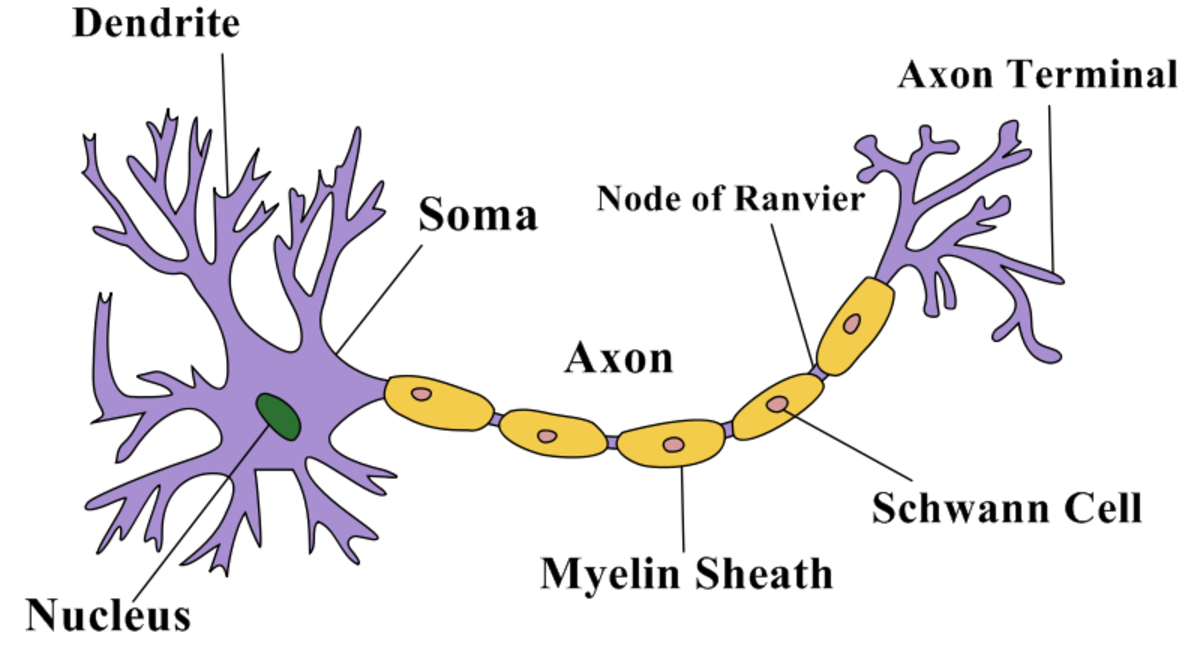
In the neuron drawing shown below, the neuron is labeled to show structures such as the cell body, axons, dendrites, and synapses. A detailed diagram of a neuron, showing the synapse, cell body.
Structure of a Neuron Owlcation
There are three main types of neurons: Motor neurons make the connection between the brain and muscles throughout the body. These neurons transmit electrical impulses containing information to skeletal muscles and smooth muscles. Motor neurons control all of our body movement. Sensory neurons are neurons that let us feel sensation.
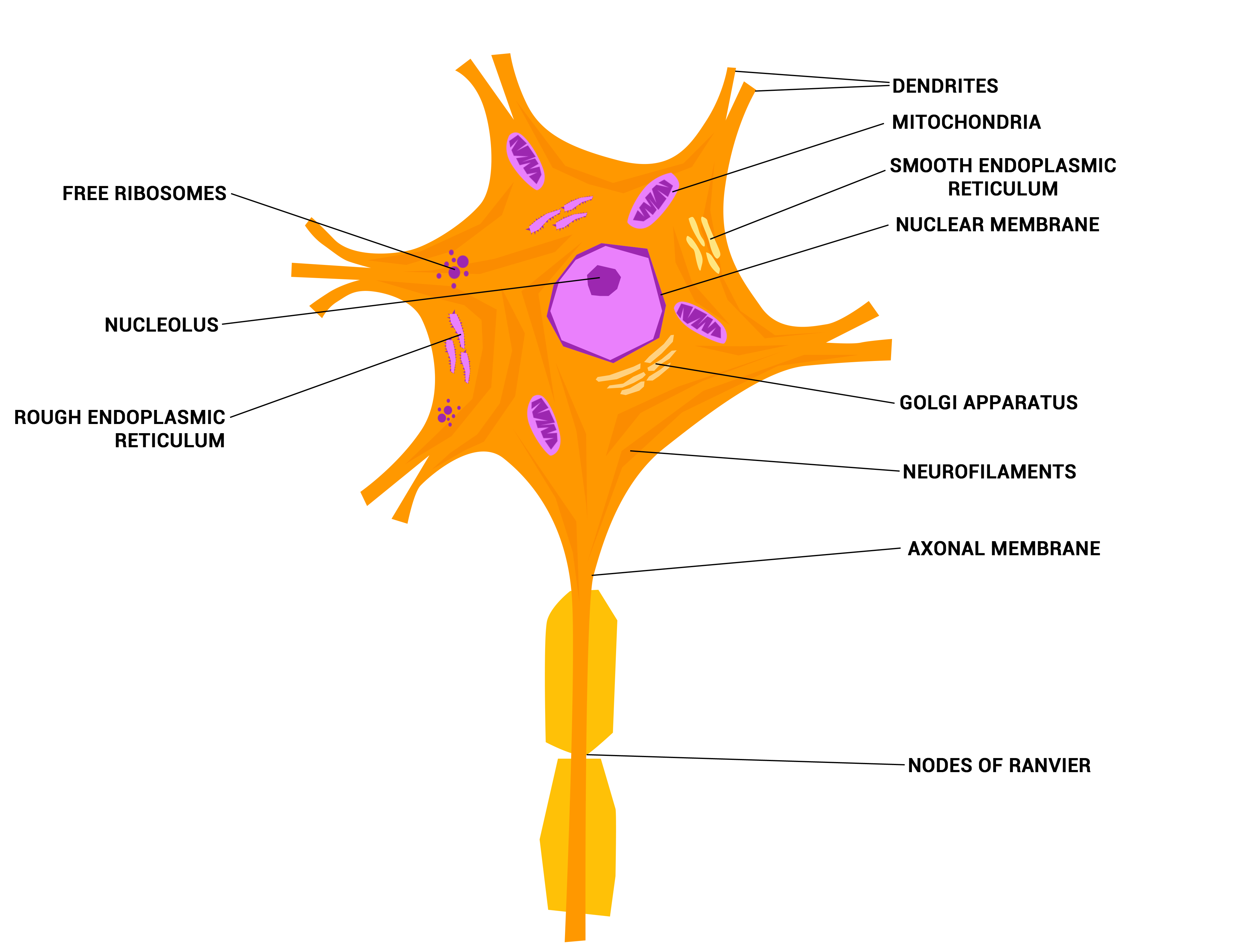
Neurons The crazy wires in our body. Doc Jana
Cerebellum - molecular, Purkinje, granular layers. Peripheral nerves - epineurium, perineurium, endoneurium. This article will explain the histology of neurons, providing you with information about their structure, types, and clinical relevance. It will also cover briefly the histological layers of the central and peripheral nervous systems.

Health Lab 4.1 Introduction
Axon. The axon, also called a nerve fiber, is a tail-like structure of the neuron that joins the cell body at a junction called the axon hillock. The function of the axon is to carry signals away from the cell body to the terminal buttons to transmit electrical signals to other neurons. Acting as a conduit, the axon carries these signals to.