Buy The Dogs Body Systems A DoubleSided, UV Protected, Laminated Dog
Dog anatomy with visible organs on white background, digital
Fast and Free Shipping On Many Items You Love On eBay. Looking For Dogs For Dogs? We Have Almost Everything On eBay.

Dog Internal Organs Anatomy Anatomy Of A Male Dog Stock Photo
Quick idea: in this article, you will learn the location of different organs from the different systems (like skeletal, digestive, respiratory, urinary, cardiovascular, endocrine, nervous, and special sense) of a dog with their important anatomical features.
Internal Organs Of A Male Dog. From Photograph by Ken Welsh
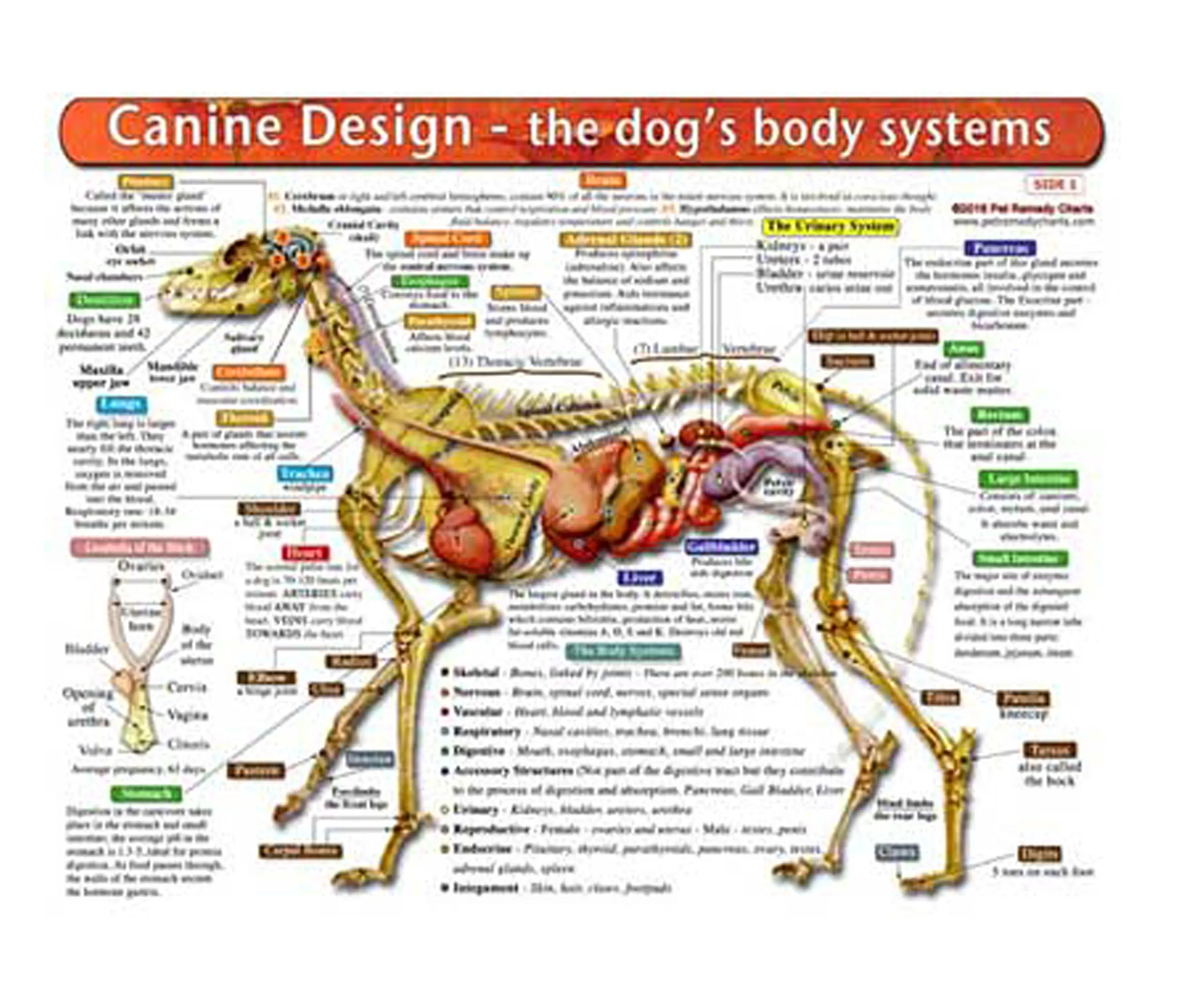
One of the most important parts of a dog's anatomy is their skeleton. A dog's skeleton is made up of many different bones, which provide structure and support for their body. Dogs have over 300 bones in their body, which is more than humans who have around 206 bones. Their skeleton includes their skull, spine, ribcage and limbs.
Coughing in Dogs May Signal Heart Disease HubPages
Our 3D anatomy application is a fully-featured virtual reality anatomy atlas. It is an immersive self-discovery experience into animal body’s. You can manipulate bones, muscles, vessels, organs and other anatomical structures. Examine them closely from all angles, read their anatomical terminology and read descriptive texts. Delve into the body systems, peek under the skin, and see what.
Buy The Dogs Body Systems A DoubleSided, UV Protected, Laminated Dog
A dog's limbs, paws, and claws are marvels of evolutionary adaptation. Dogs usually have four toes on their rear paws and five on their front paws (including the dewclaw). The structure of the limbs and paws allows for a range of movements, from rapid acceleration and deceleration to agile turns and jumps.
finearts304 dogs organs
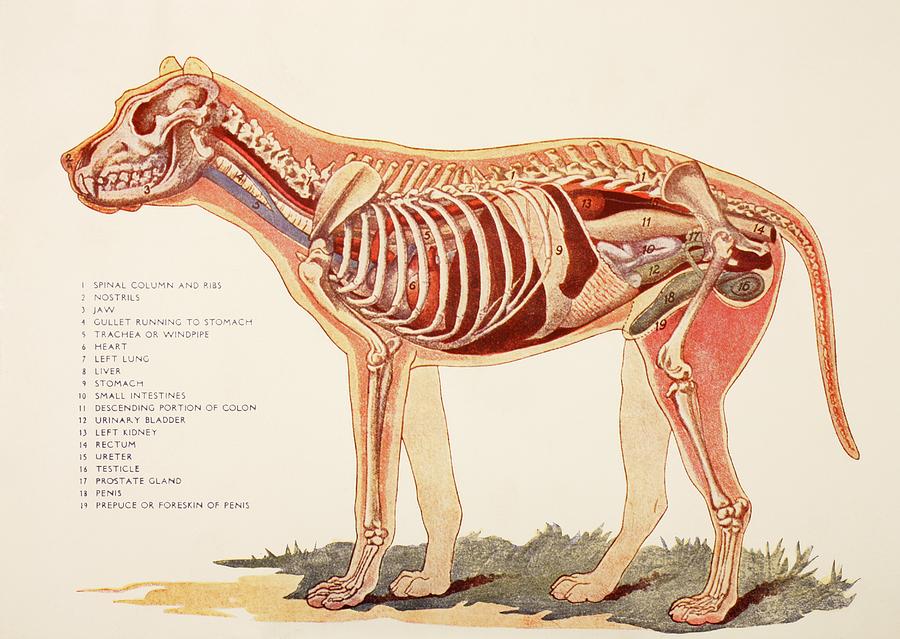
Veterinary anatomy - Animal: ANATOMICAL PARTS Abdomen Abdominal aorta Abdominal mammary gland Abdominal mammary region Accessory carpal bone Acromion Adductor muscle Ala of ilium; Wing of ilium Ala of nose Anconeus muscle Antebrachial region Aortic arch Apex of nose; Tip of nose Arm
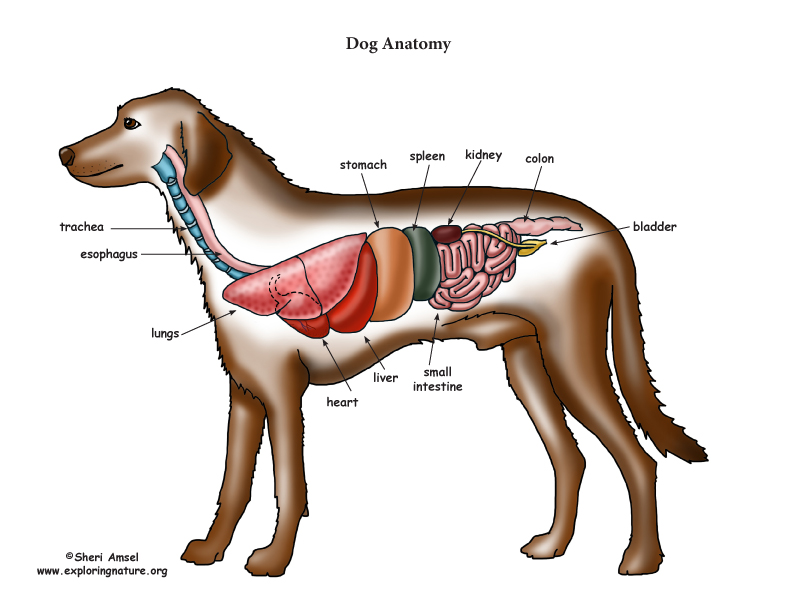
Dog Anatomy (Thoracic and Abdominal Organs)
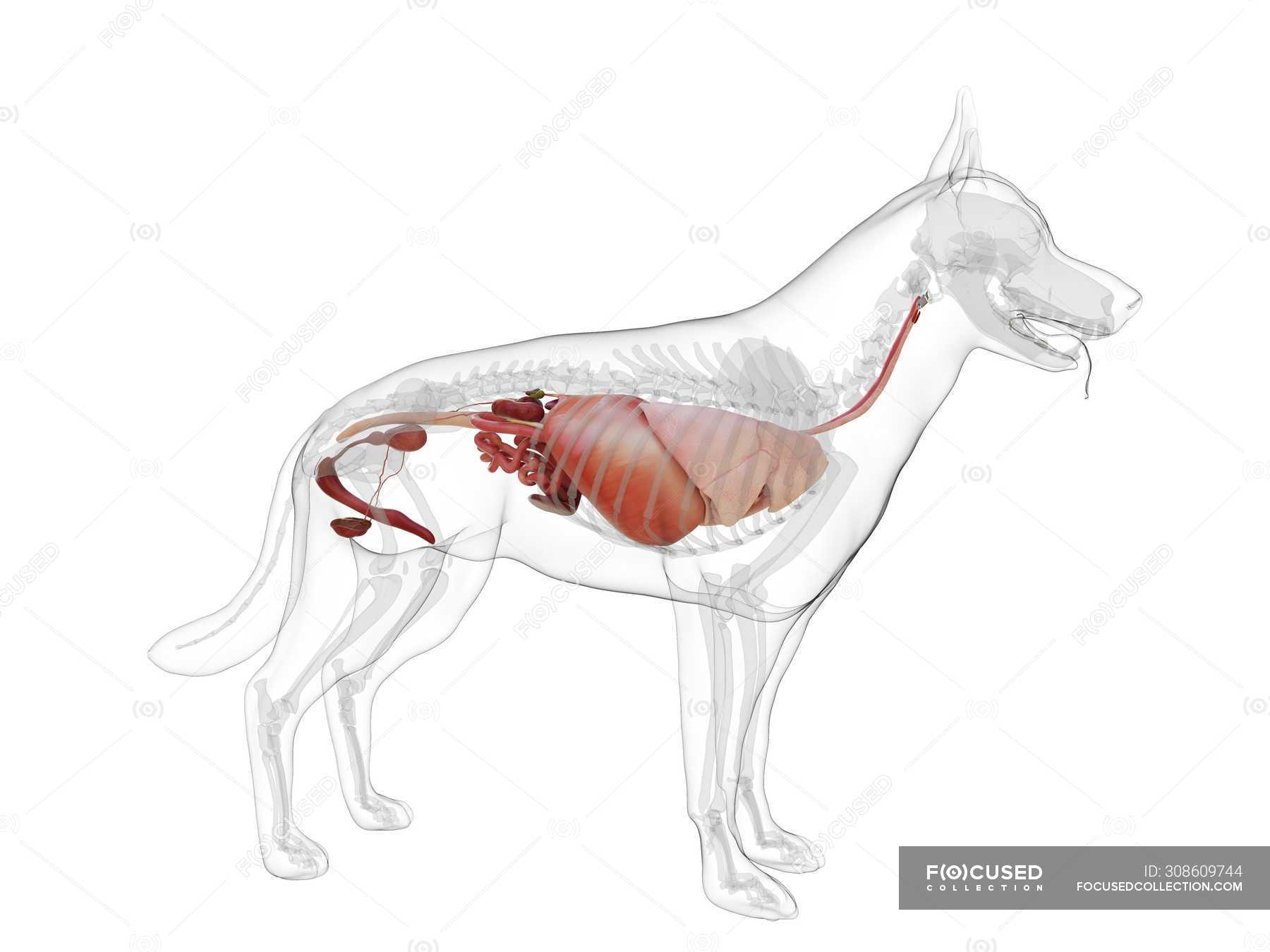
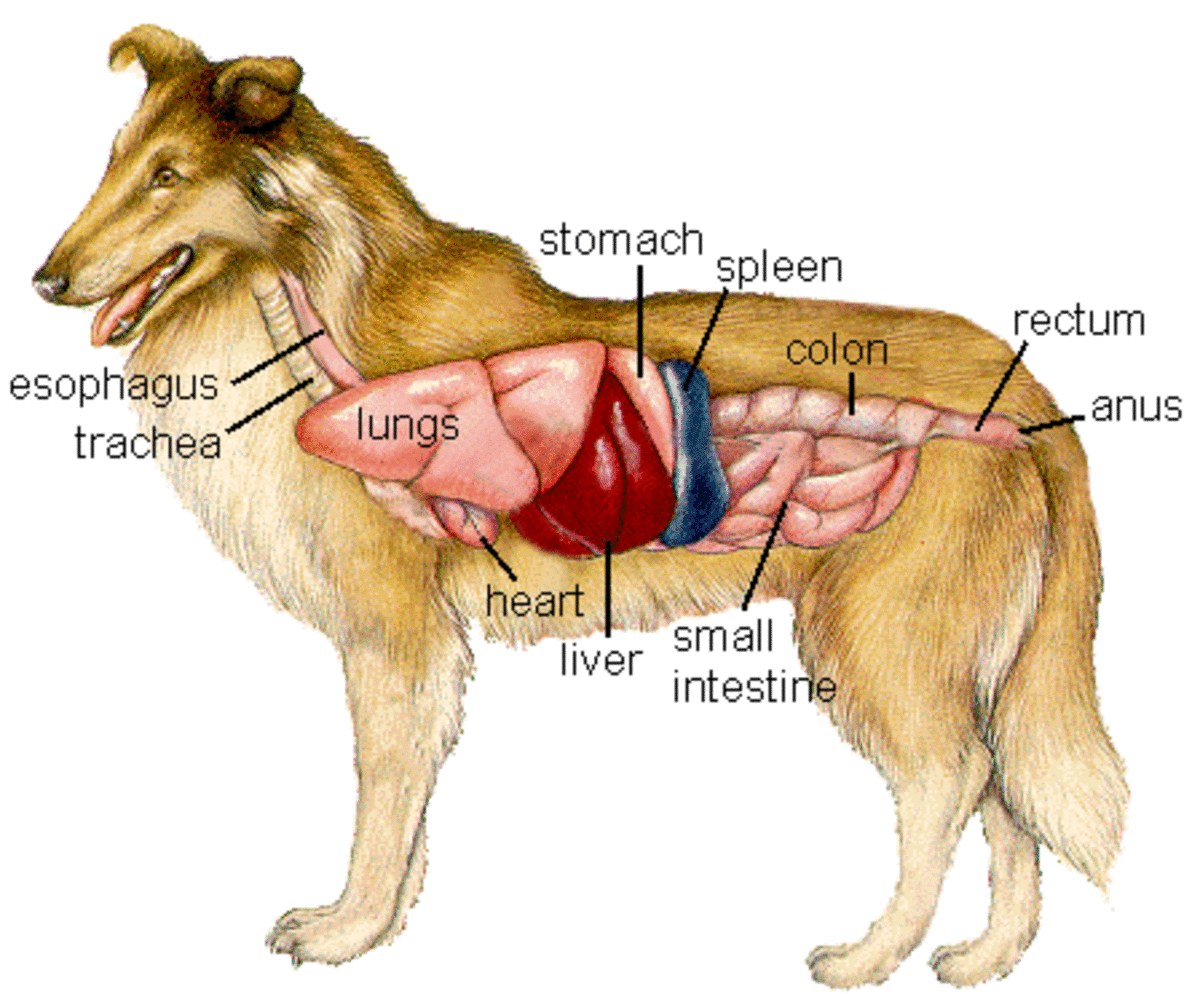
On the left side view of a dog's internal organs, you can see the lungs, heart, liver, stomach, spleen, kidney, intestines, bladder, and the rectum in that order from front to back. You can also view the spinal column and the brain. Laurie O'Keefe Dog Anatomy Organs Right Side

Dog Anatomy Internal Organs Stock Image Z932/0462 Science Photo
Hearing: Dogs have a greater hearing range than people do. They can detect sound as low as 16 Hz frequency to as high as 100,000 Hz (people hear 20 to 20,000 Hz ).

Anatomy of a male dog crosssection, showing the skeleton and internal
Summary Anatomy of a Dog Dog anatomy details the various structures of canines (e.g. muscle, organ and skeletal anatomy). The detailing of these structures changes based on dog breed due to the huge variation of size in dog breeds. Would you be surprised to know that short dogs are more aggressive? Or taller dogs are more affectionate?
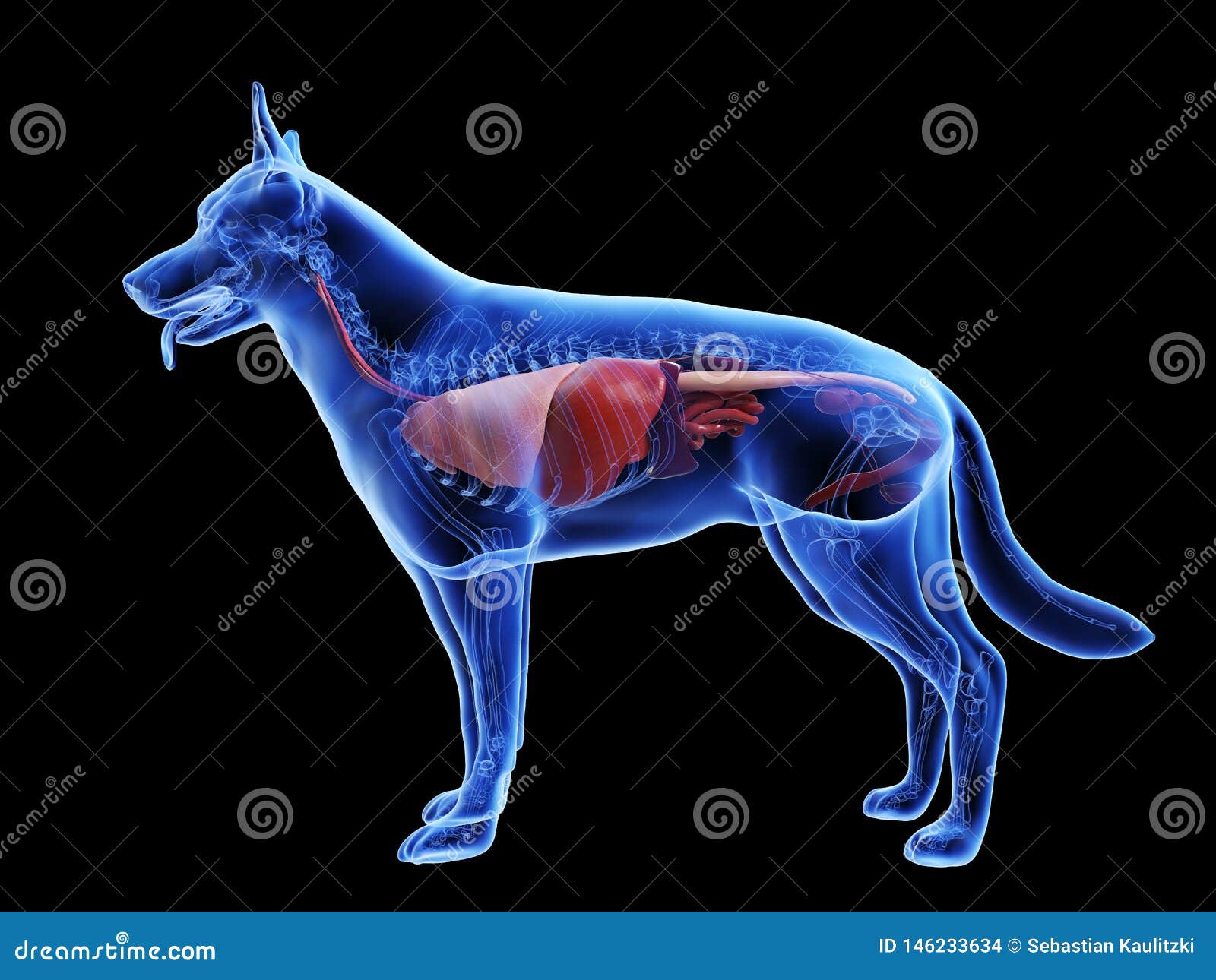
A dogs internal organs stock illustration. Illustration of medical
Canine anatomy Dog skeleton Muscles of the dog Organs of dogs Canine anatomy As we explain above, canine anatomy is far ranging due to the diversity of existing breeds. These different breeds not only differ from each other in size, but in the shape of many body parts. Perhaps the most significant is head shape.

Anatomy Of Back Organs / Anatomy Male Organs in Loop Stock Footage
We will be covering the most commonly used body parts of a dog, including the abdomen, throat, back, nape, belly, brisket, wrist, chest, prosternum, croup, claw, ear, elbow, and many more. Our aim is to provide you with a comprehensive understanding of the different parts of a dog's anatomy. This knowledge will help you identify any potential.
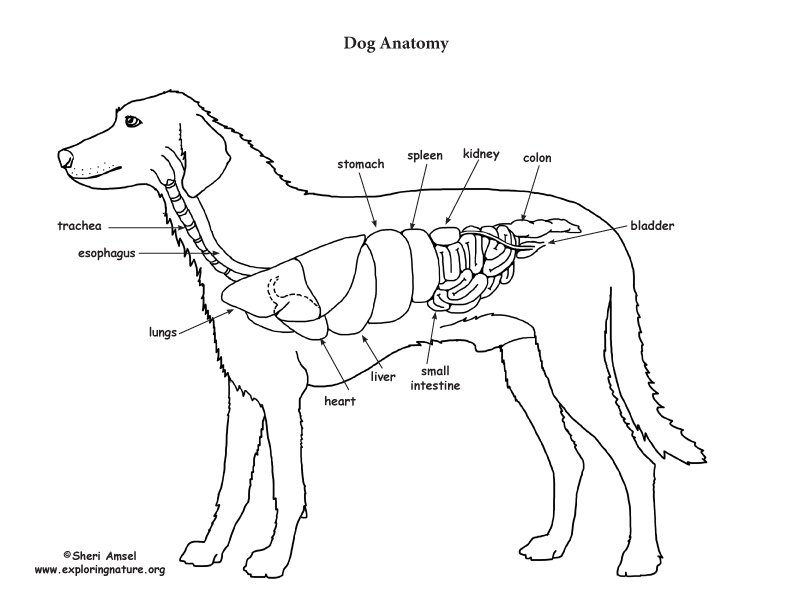
Dog Anatomy (Thoracic and Abdominal Organs)
Anatomic Planes. The main planes of motion for dogs are as follows (see Figure 5-1): • The sagittal plane divides the dog into right and left portions. If this plane were in the midline of the body, this is the median plane or median sagittal plane. • The dorsal plane divides the dog into ventral and dorsal portions.
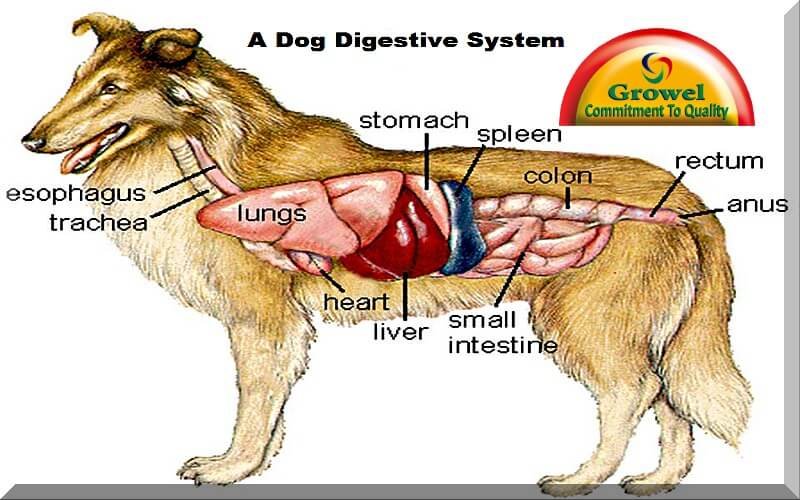
A Dog Digestive System Growel Agrovet
Internal anatomy of a dog: carnivorous domestic mammal raised to perform various tasks for humans. Encephalon: seat of the intelluctual capacities of a gog. Spinal column: important part of the nervous system. Stomach: part of the digestive tract between the esophagus and the intestine. Spleen: hematopoiesis organ that produces lymphocytes.

Dog Internal Organ Anatomy Poster Chart Zazzle
Dog Anatomy - Internal Organs. Z932/0462. Rights Managed. 14.9 MB (591.0 KB compressed) 2592 x 2004 pixels. 21.8 x 17.0 cm · 8.6 x 6.7 in (300dpi) Request Price Add To Basket ADD TO BOARD.

Внутренние органы собаки. Вид справа Dog Internal Organs, Anatomy
Xiphoid region (Cranial abdominal region) Zygomatic bone. Zygomatic gland. Zygomatic region. Radiographic anatomy: labeled images in the transverse plane of a healthy dog's whole body, using tomodensitometry. Introduction to the anatomy of the skull, thorax, abdomen, pelvic cavity, muscles and blood vessels: main anatomical structures identified.

an animal's skeletal and muscular muscles are shown in this diagram
Give the Gift of Independence this Holiday Season. Donate to our Christmas Appeal today! Help Us Change Lives. Your Donation can Provide Freedom and Confidence to Someone in Need!