Anatomy Of Human Skin With Labels Photograph by Hank Grebe Pixels

Dermis Layers, Papillary Layer, Function Epidermis
Above: Skin cross section diagram showing the epidermis with melanocytes (pigment cells), dermis, and hypodermis (fatty tissue) layers as well as glands, hairs, and blood vessels embedded in these tissue layers. The skin is also called the cutaneous membrane. There are two types of skin: thin skin that is covered with hair (also contains.
Schematic representation of skin structure and cell population. The... Download Scientific Diagram
The Epidermis The epidermis is composed of keratinized, stratified squamous epithelium. It is made of four or five layers of epithelial cells, depending on its location in the body. It does not have any blood vessels within it (i.e., it is avascular). Skin that has four layers of cells is referred to as "thin skin."
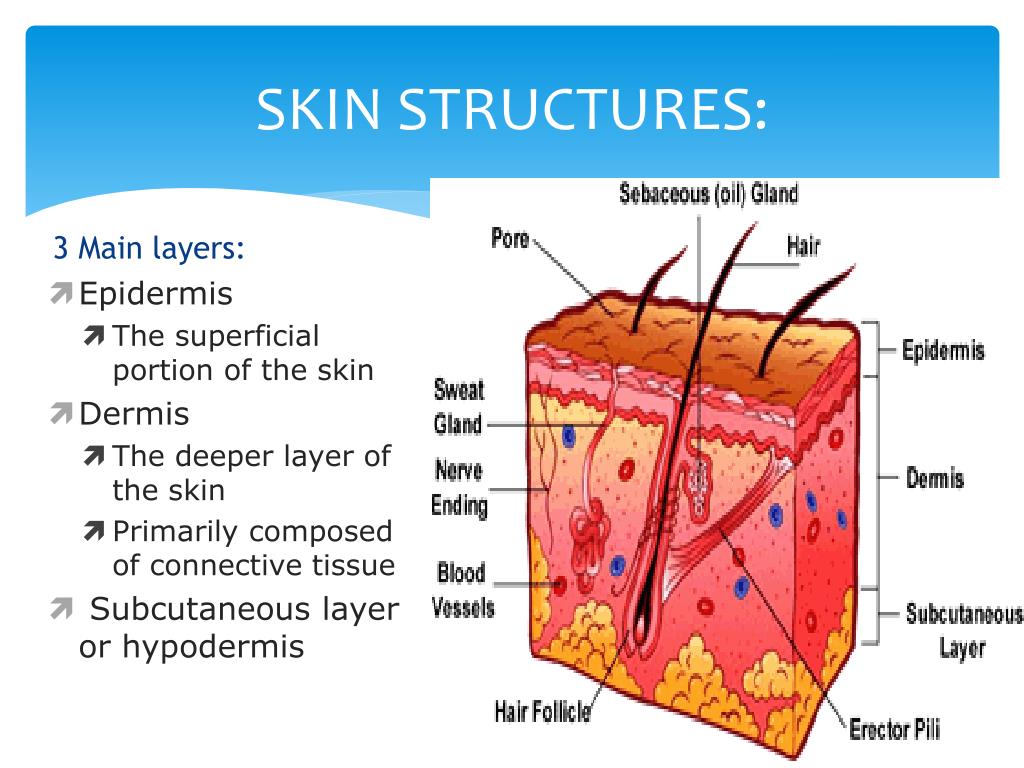
PPT Basic Skin Structure PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID6099891
Dermatology nomenclature Desquamation imbalance Psoriasis Albinism Sources + Show all Without the skin, humans would be susceptible to a myriad of pathologies. The organ acts as a protective barrier that limits the migration of microbes and chemicals into the body.

The Structure Of Human Skin Cells Stock Illustration Download Image Now Hair Follicle
The Dermis Hypodermis The number of skin layers that exists depends on how you count them. You have three main layers of skin—the epidermis , dermis, and hypodermis (subcutaneous tissue). Within these layers are additional layers. If you count the layers within the layers, the skin has eight or even 10 layers.

Structure Of Skin Skin Structure and Function LearnFatafat
The skin is the body's largest organ, made of water, protein, fats and minerals. Your skin protects your body from germs and regulates body temperature. Nerves in the skin help you feel sensations like hot and cold. Your skin, along with your hair, nails, oil glands and sweat glands, is part of the integumentary (in-TEG-you-ME I NT-a-ree) system.

The skin Understanding cancer Macmillan Cancer Support
Dermis. Definition. Fibrous and elastic tissue, provides strength and elasticity to the skin and supports the epidermis, home to hair follicles, glands, nerves etc. Location. Term. Papillary Layer. Definition. Upper dermal layer, provides the epidermis with nutrients and regulates body temperature. Location.
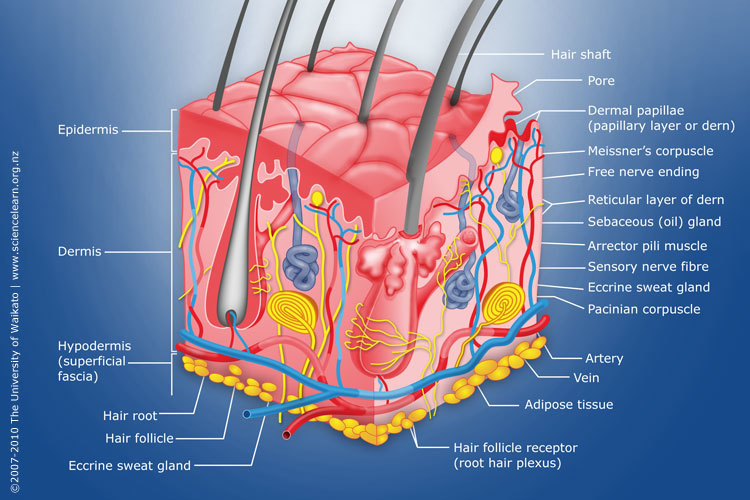
Diagram of human skin structure — Science Learning Hub
Stratum basale, also known as stratum germinativum, is the deepest layer, separated from the dermis by the basement membrane (basal lamina) and attached to the basement membrane by hemidesmosomes. The cells found in this layer are cuboidal to columnar mitotically active stem cells that are constantly producing keratinocytes.
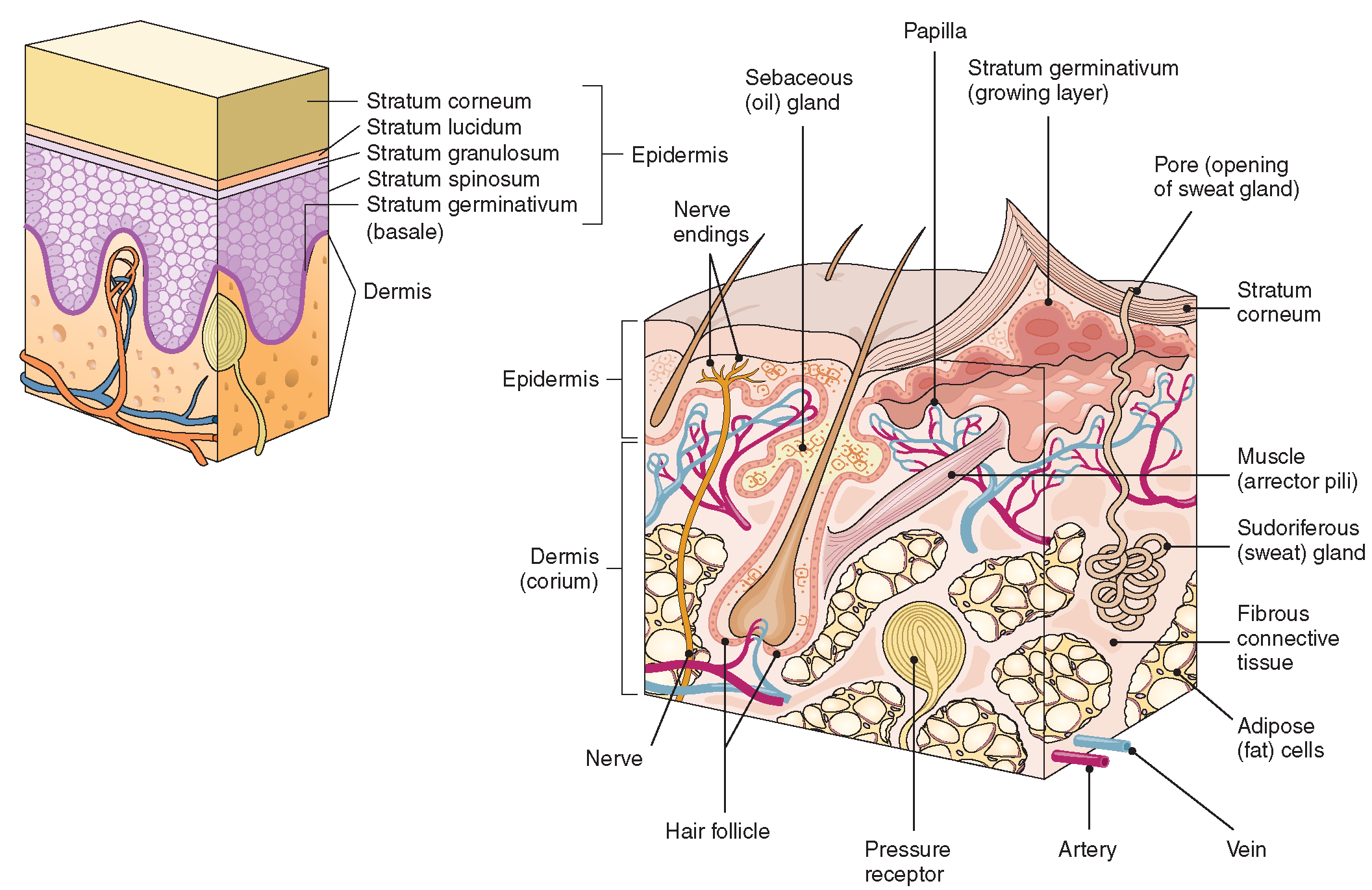
The Integumentary System (Structure and Function) (Nursing) Part 1
The skin is the body's largest and primary protective organ, covering its entire external surface and serving as a first-order physical barrier against the environment. Its functions include temperature regulation and protection against ultraviolet (UV) light, trauma, pathogens, microorganisms, and toxins. The skin also plays a role in immunologic surveillance, sensory perception, control of.

The structure of the skin is composed of two layers (1) the epidermis... Download Scientific
Explore Skin Diagram with BYJU'S. Diagram of the skin is illustrated in detail with neat and clear labelling. Also available for free download

Skin Definition, Structure And Functions Of Skin
Reading time: 16 minutes Recommended video: Integumentary system [19:28] Structure and layers of the skin. Thick skin 1/10 Synonyms: none The integumentary system is the body system which surrounds you, both literally and metaphorically speaking.

Skin layers structure anatomy diagram human Vector Image
Label Me! Printout The skin is an organ that forms a protective barrier against germs (and other organisms) and keeps the inside of your body inside your body, and keeps what's outside of your body outside. Skin also helps maintain a constant body temperature. Human skin is only about 0.07 inches (2 mm) thick.

Anatomy of human skin. The most superficial layer of the skin is the... Download Scientific
This diagram shows the layers found in skin. There are three main layers: the epidermis, dermis and hypodermis. There are also sweat glands, and hairs, which have sebaceous glands, and a smooth muscle called the arrector pili muscle, associated with them.
Skin diagram to label Labelled diagram
Skin is part of the integumentary system and considered to be the largest organ of the human body. There are three main layers of skin: the epidermis, the dermis, and the hypodermis (subcutaneous fat). The focus of this topic is on the epidermal and dermal layers of skin.
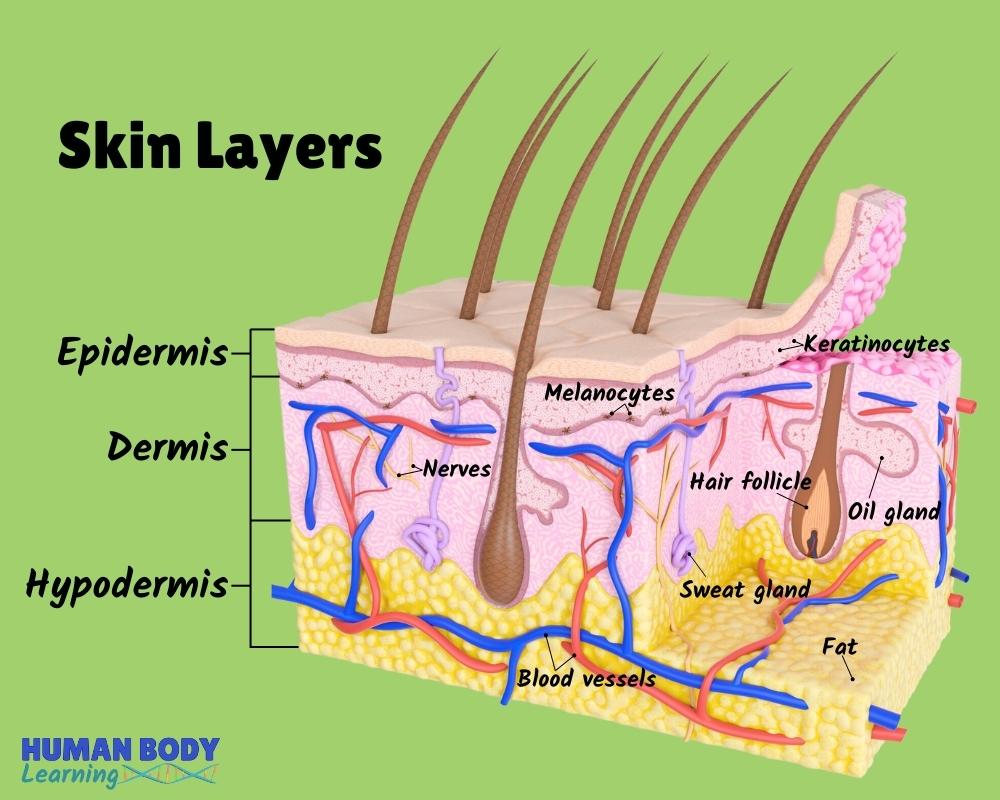
Skin Layers Anatomy Diagram for Kids
This Osmosis High-Yield Note provides an overview of Skin Structures essentials. All Osmosis Notes are clearly laid-out and contain striking images, tables, and diagrams to help visual learners understand complex topics quickly and efficiently. Find more information about Skin Structures: Skin anatomy and physiology. Hair, skin and nails.
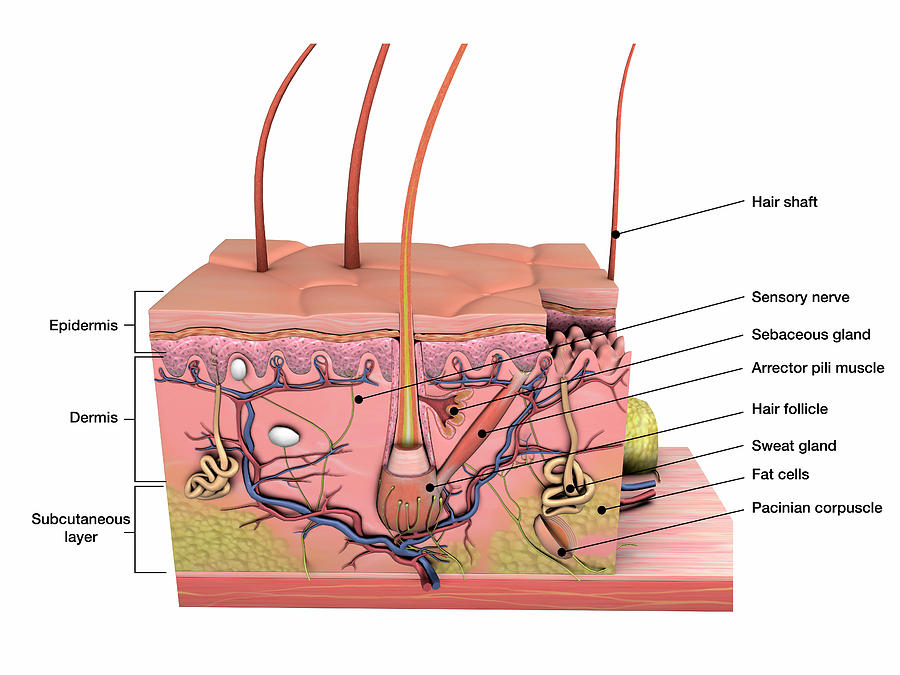
Anatomy Of Human Skin With Labels Photograph by Hank Grebe Pixels
The epidermis is the thin outer layer of the skin. It consists of 2 primary types of cells: Keratinocytes. Keratinocytes comprise about 90% of the epidermis and are responsible for its structure and barrier functions. Melanocytes. Melanocytes are found at the base of the epidermis and make melanin. This gives the skin its color. Dermis

Human skin diagram Subcutaneous tissue, Skin structure, Epidermis
Facts about the skin. The skin is the body's largest organ. It covers the entire body. It serves as a protective shield against heat, light, injury, and infection. The skin also: Regulates body temperature. Stores water and fat. Is a sensory organ. Prevents water loss. Prevents entry of bacteria. Acts as a barrier between the organism and its.