Energy gap of graphene. (a) The schematic diagram of band dispersion at... Download Scientific
Band gap energy and band gap edge positions of different semiconductor... Download Scientific
Semiconductors are defined by their name: they are kinda conductive. These materials have a band gap, but it's not as big as that of an insulator. Often in the field, 3 eV 3 e V serves as a rough cut-off: band gaps below this energy belong to semiconductors, while higher energy systems are considered insulating.
Top Variations of (a) energy gaps and (b) relative energies among... Download Scientific Diagram
How does the band gap energy vary with composition?There are two important trends (1) Going down a group in the periodic table, the gap decreases:. C (diamond) > Si > Ge > α-Sn. E gap (eV): 5.4 1.1 0.7 0.0. This trend can be understood by recalling that E gap is related to the energy splitting between bonding and antibonding orbitals.This difference decreases (and bonds become weaker) as the.

Four energy gap functions depending on the 'Te' concentration. Download Scientific Diagram
The separation between the conduction band and valence band on the energy band diagram is known as the forbidden energy gap (band-gap, E g ). The width of the energy gap is a measure of the bondage of valence electrons to the atom. The greater the energy gap, the more tightly the valence electrons are bound to the nucleus.
6 Energy band structures of GaAs and silicon as in [5]. A... Download Scientific Diagram
An extension of the simple band energy diagram with only the vertical axis labelled as energy, with the horizontal axis unlabelled, is to plot the energy vertically against wave vector, k. From de Broglie's relationship p = hk where p is momentum and h is Planck's constant, h, divided by 2 π. Such plots therefore relate energy to momentum.

photochemistry What is the explanation of the energy gap law in radiationless transitions
Figure 9.6.2 9.6. 2: The dependence of energy-level splitting on the average distance between (a) two atoms, (b) four atoms, and (c) a large number of atoms. For a large number of electrons, a continuous band of energies is produced. Energy bands differ in the number of electrons they hold. In the 1 s and 2 s energy bands, each energy level.

The band gap energy alteration of TiO2/20WO3 composites. Reprinted and... Download Scientific
9:E-K Diagram, Band Gap, Effective Mass 5 From Principles of Electronic Materials and Devices, Third Edition, S.O. Kasap (© McGraw-Hill, 2005) Energy Gap (Bandgaps, Eg) Fig 4.54 S a E k [ 11] 3 E k 1 [ 10] B and B and E nergy gap E nergy gap B and B and F i rst B ri l l oui n Z one S econd B ri l l oui n Z one S econd B ri l l oui n Z one F i.

Contour diagram of fundamental energy gaps in strained Si 1Àx Ge x over... Download Scientific
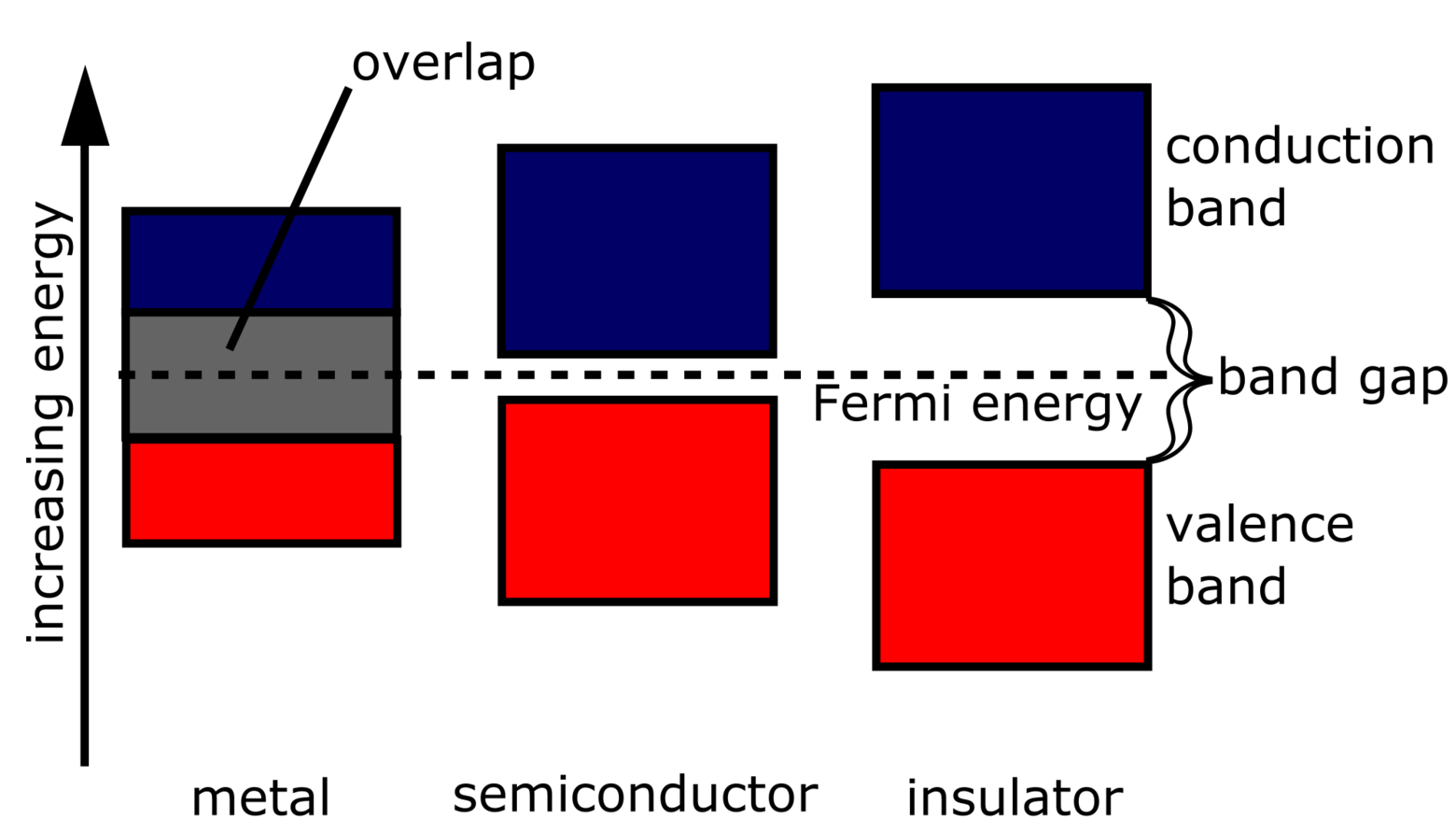
A semiconductor has a similar energy structure to an insulator except it has a relatively small energy gap between the lowest completely filled band and the next available unfilled band. This type of material forms the basis of modern electronics. At T = 0 K T = 0 K, the semiconductor and insulator both have completely filled bands.The only difference is in the size of the energy gap (or band.

Bandgap energetics diagram of (a) ZnO and (b) ZnOgraphene or ZnOCNT... Download Scientific
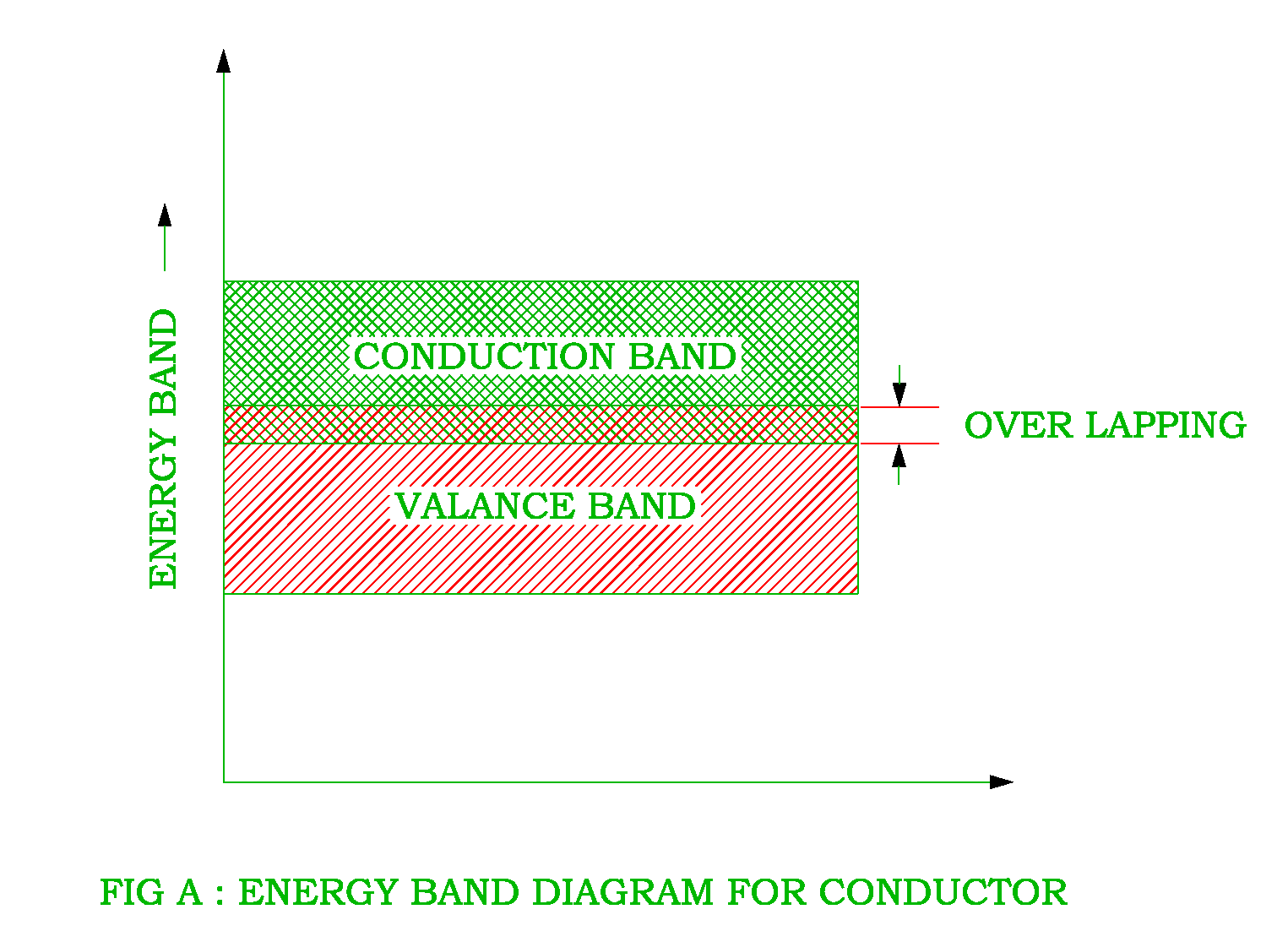
The energy band gap is the energy difference between a material's valence and conduction bands. Conductors have overlapping valence and conduction bands, allowing electrons to move quickly through the material and conduct electricity. Examples of conductors include copper (Cu), aluminum (Al), and silver (Ag).

1. (a) Energy band diagram of AlGaN/GaN HEMT illustrating band gap... Download Scientific Diagram
The energy gap in the insulator is very high up to 7eV. The material cannot conduct because the movement of the electrons from the valence band to the conduction band is not possible.. The energy band diagram of semiconductors is shown where the conduction band is empty and the valence band is completely filled but the forbidden gap between.

Energy band diagram for perovskite solar cell on a scaffold structure... Download Scientific
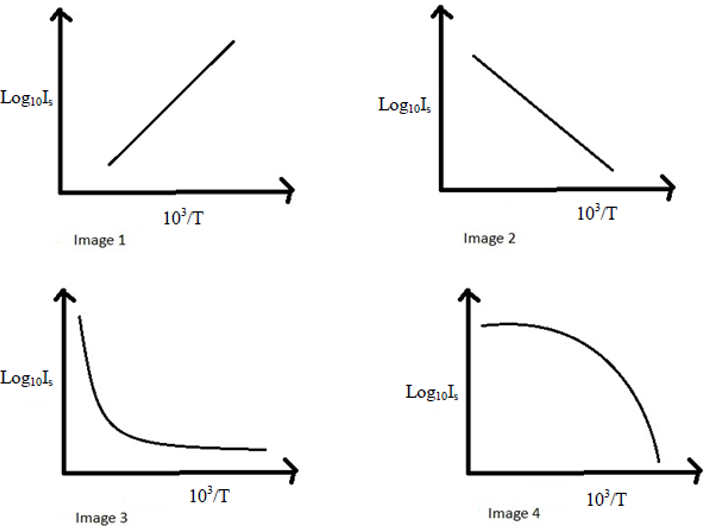
What information can we get from the band diagrams? 1. Allowed and forbidden bands. Identification of the gap energy. 2. Slope of the bands - group velocity. 3. Curvature of bands - effective mass. 1. Magnitude of the band gaps: Larger atoms smaller potential smaller bandgap. 2. Group velocity Let's examine the form of the energy.
Energy Band Gap Simulation
The band gap (E G) is the gap in energy between the bound state and the free state, between the valence band and conduction band. Therefore, the band gap is the minimum change in energy required to excite the electron so that it can participate in conduction. Schematic of the energy bands for electrons in a solid.

2 Energy bandgap diagram Download Scientific Diagram
In solid-state physics and solid-state chemistry, a band gap, also called a bandgap or energy gap, is an energy range in a solid where no electronic states exist. In graphs of the electronic band structure of solids, the band gap refers to the energy difference (often expressed in electronvolts ) between the top of the valence band and the bottom of the conduction band in insulators and.
band gap diagram electric field
Direct band gap: the lowest-energy state above the band gap has the same k as the highest-energy state beneath the band gap.. When the horizontal lines in these diagram are slanted then the energy of the level or band changes with distance. Diagrammatically, this depicts the presence of an electric field within the crystal system..
Band gap Energy Education
In a direct band gap semiconductor, the top of the valence band and the bottom of the conduction band occur at the same value of momentum, as in the schematic below. In an indirect band gap semiconductor, the maximum energy of the valence band occurs at a different value of momentum to the minimum in the conduction band energy: The difference.
Energy band diagram demonstrating different band gap energies. Download Scientific Diagram
A band gap is the distance between the valence band of electrons and the conduction band. Essentially, the band gap represents the minimum energy that is required to excite an electron up to a state in the conduction band where it can participate in conduction. [1] The lower energy level is the valence band, and thus if a gap exists between.

Energy gap of graphene. (a) The schematic diagram of band dispersion at... Download Scientific
1-1. Energy band diagram. 1-1. Energy band diagram. Free electrons in a material allow a free flow of electricity. Although being part of atoms, free electrons are so loosely bound to atoms in a material, they can move about freely. In classical physics, the Bohr model is a physical model that consists of a small atomic nucleus of protons and.