On This Day 200th anniversary of the birth of Florence Nightingale

the lady with the lamp Florence nightingale, History of nursing, Nightingale
Florence Nightingale was born on May 12, 1820 in the Italian city of Florence and named after that city. She was the daughter of a wealthy British couple who were enjoying an extended stay in Italy on their Grand Tour of classical Europe - a popular activity with the upper classes of that era. She had an older sister, Frances.

Portrait of Florence Nightingale Collection
Florence Nightingale, 1820-1910. Florence Nightingale dedicated much of her life to the reform of the British military healthcare system. Her practices brought tremendous respect to the field of nursing, and she made great strides in the reform of hospital sanitation. Intensely charismatic and inspirational, Florence Nightingale was an.

The Lady with the Lamp Florence Nightingale One Day Creative
Florence Nightingale understood the power of visualizing science She illustrated that simple sanitation techniques could stop the spread of infectious diseases Florence Nightingale would have.
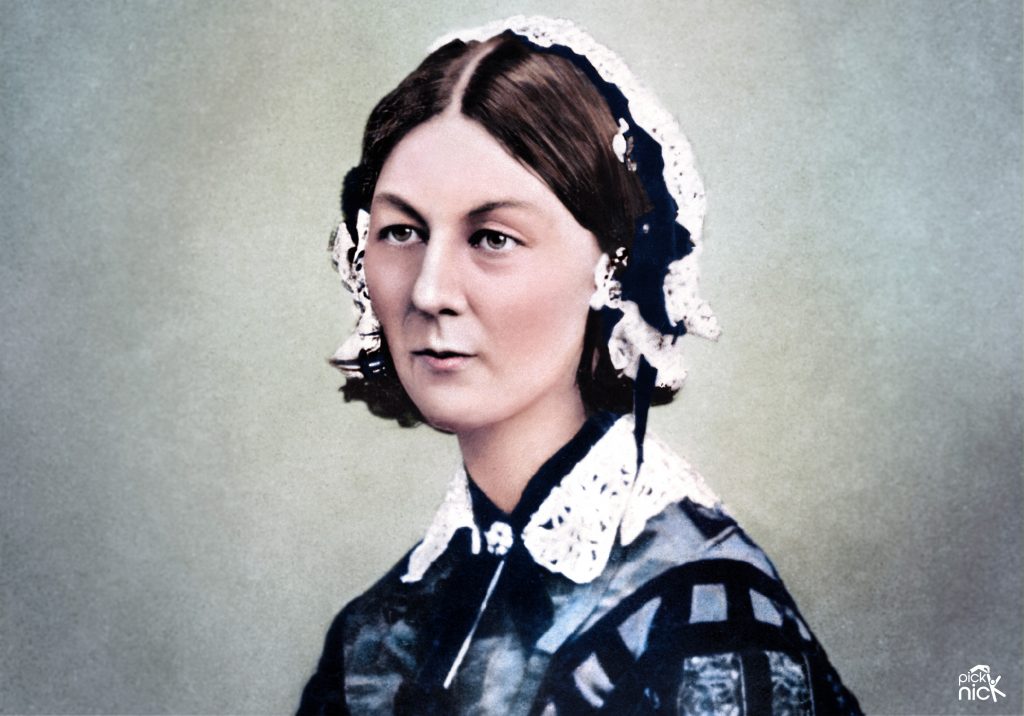

On This Day 200th anniversary of the birth of Florence Nightingale
(1820-1910) Who Was Florence Nightingale? Part of a wealthy family, Florence Nightingale defied the expectations of the time and pursued what she saw as her God-given calling of nursing..
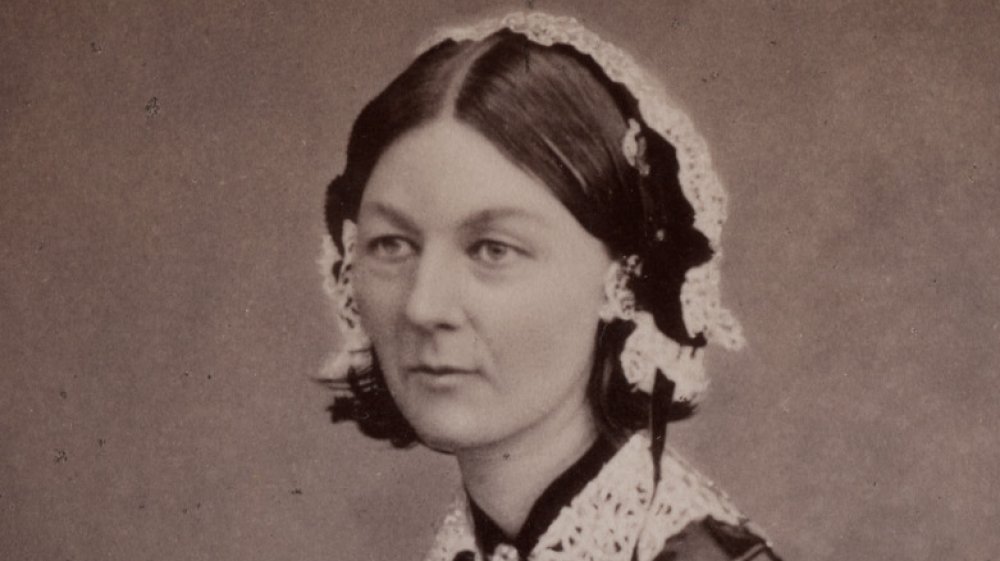
The Tragic Life Of Florence Nightingale
Florence Nightingale was born on May 12, 1820, in Florence, Italy. Although her parents were from England, she was born in Italy while they were traveling. Both Florence and her older sister Parthenope were named after the Italian cities where they were born. When they returned to England in 1821, the Nightingale family lived in two homes.

Florence Nightingale Life & Legacy a Guide for Kids
Florence Nightingale is the most recognized name in the field of nursing. Her work was instrumental for developing modern nursing practice, and from her first shift, she worked to ensure patients in her care had what they needed to get healthy. Her Environmental Theory changed the face of nursing to create sanitary conditions for patients to get care.
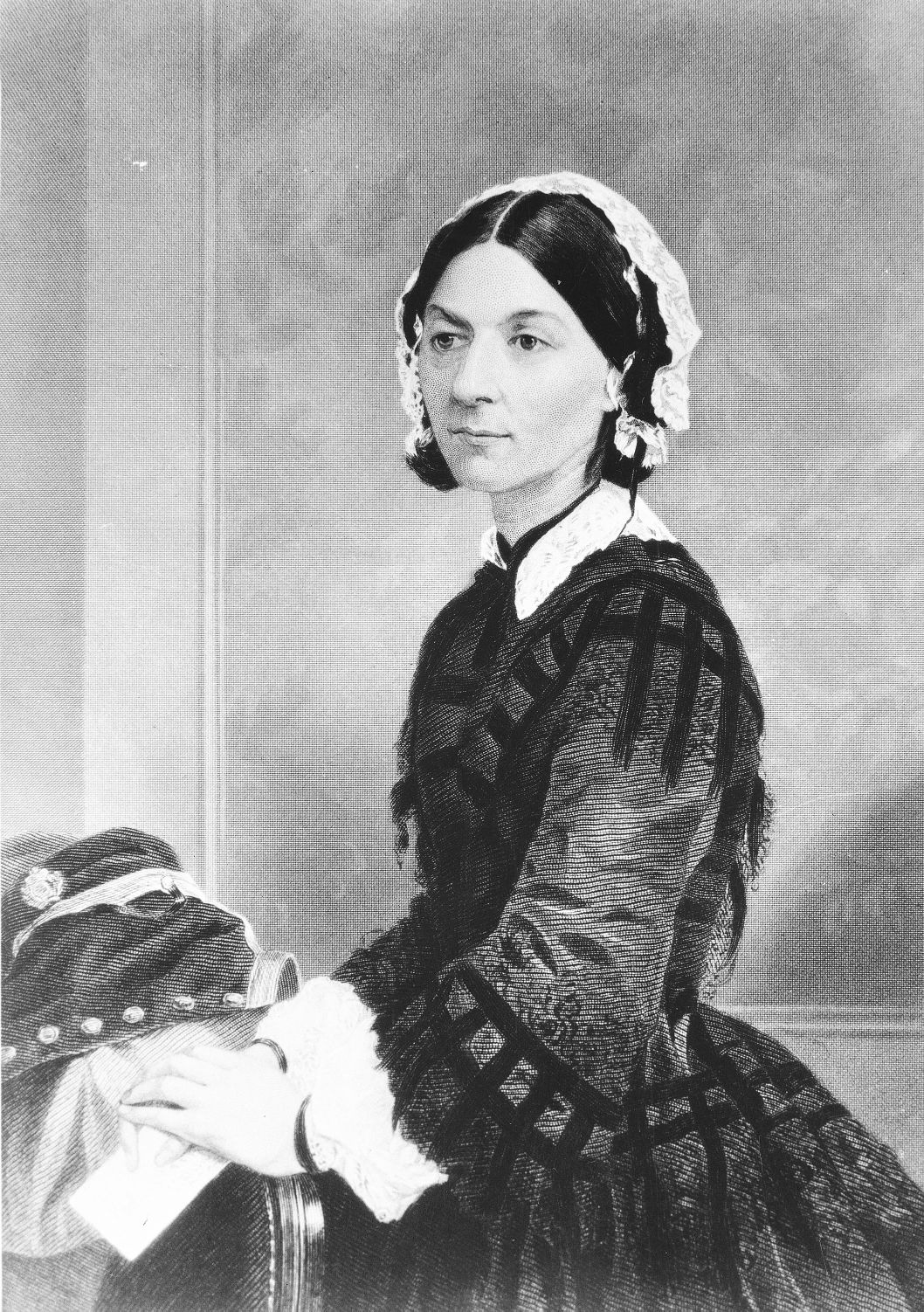
Today In History, Aug. 13 Florence Nightingale History
Florence Nightingale (1820-1910), known as "The Lady With the Lamp," was a British nurse, social reformer and statistician best known as the founder of modern nursing. Her experiences as a nurse.

Florence Nightingale The Lady with the Lamp and Pie Chart Margo Lestz The Curious Rambler
Florence Nightingale (born May 12, 1820, Florence [Italy]—died August 13, 1910, London, England) British nurse, statistician, and social reformer who was the foundational philosopher of modern nursing. Nightingale was put in charge of nursing British and allied soldiers in Turkey during the Crimean War.

200 years after her birth how Florence Nightingale founded modern nursing Express & Star
Florence Nightingale - Wikipedia ; 12 May 1820 - 13 August 1910) was an English , statistician and the founder of modern . Nightingale came to prominence while serving as a manager and trainer of nurses during the , in which she organised care for wounded soldiers at She significantly reduced death rates by improving hygiene and living standards.
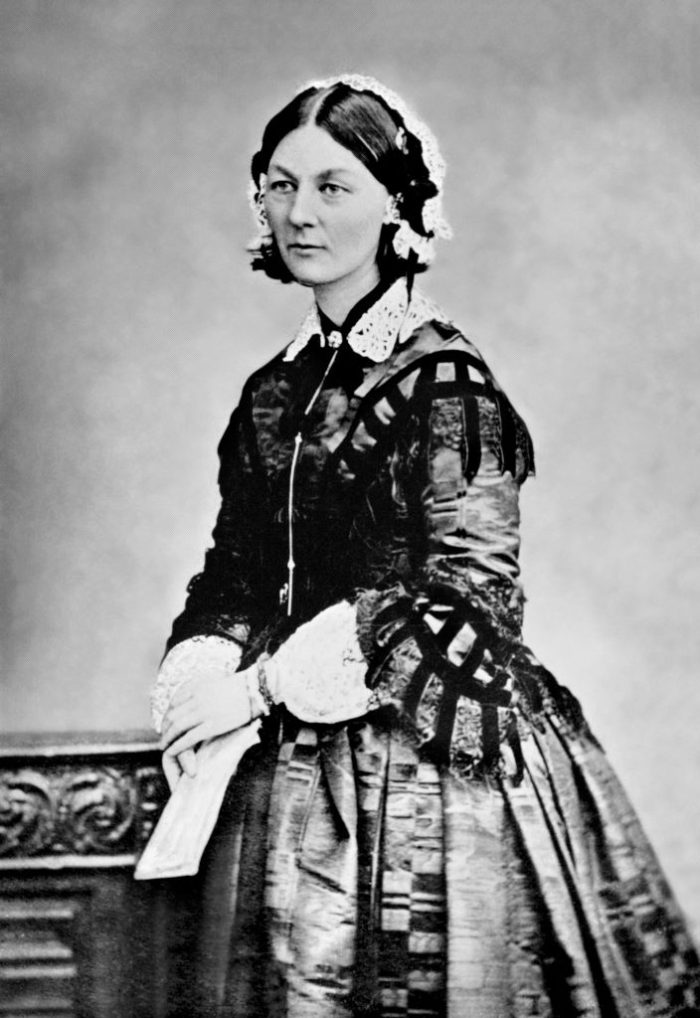

Light in the Dark Florence Nightingale's legacy Discover Britain
Florence Nightingale. Born: May 12, 1820 Florence, Italy Died: August 13, 1910 London, England English nurse. The English nurse Florence Nightingale was the founder of modern nursing and made outstanding contributions to the knowledge and improvement of public health.. Early years and study. Florence Nightingale was born in Florence, Italy, on May 12, 1820; she was named after the city of her.
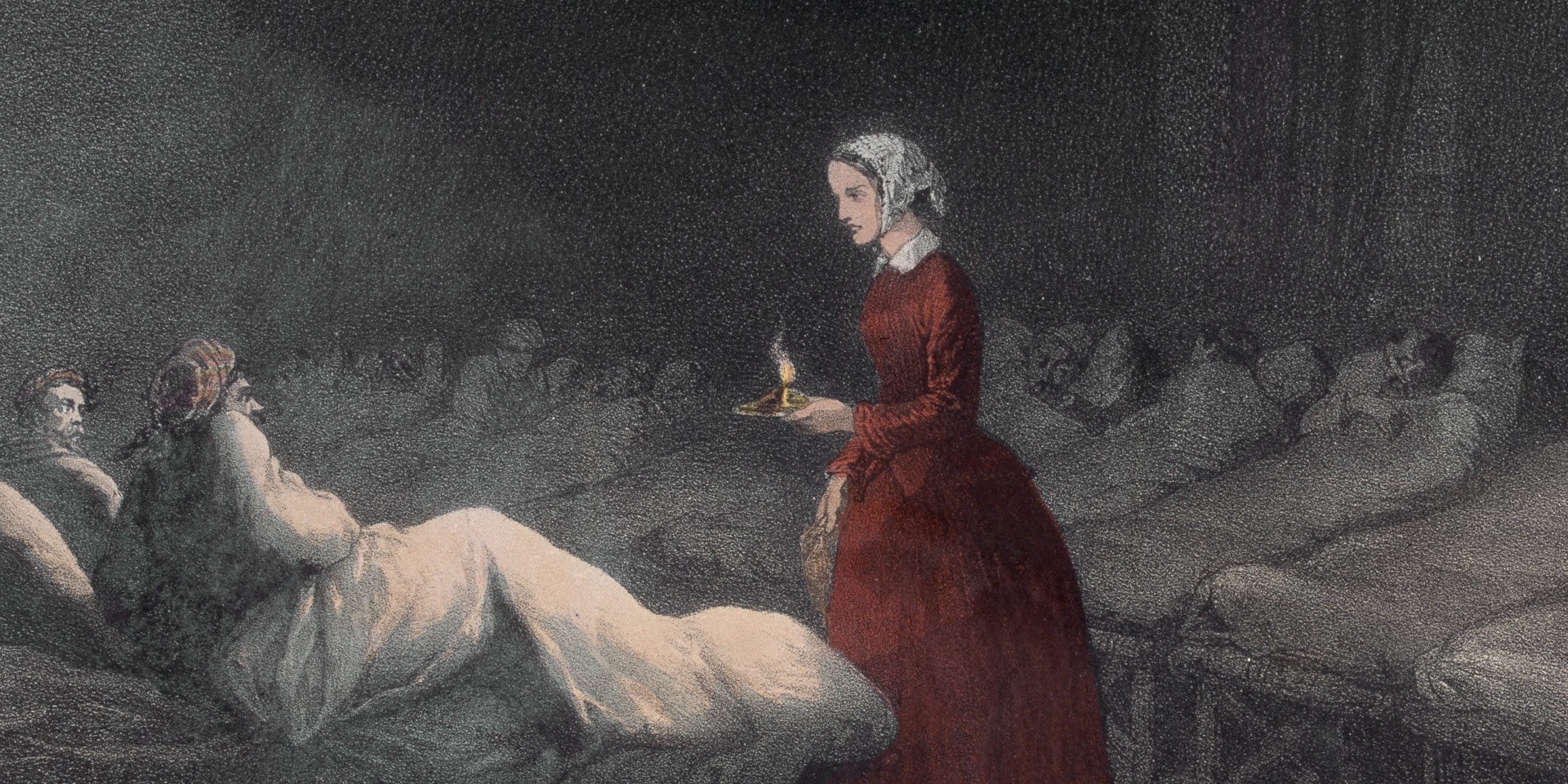

Florence Nightingale The Lady with the Lamp National Army Museum
Modern nursing is complex, ever changing, and multi focused. Since the time of Florence Nightingale, however, the goal of nursing has remained unchanged - namely to provide a safe and caring environment that promotes patient health and well being. Effective use of an interpersonal tool, such as advocacy, enhances the care-giving environment.

The Life and Legacy of Florence Nightingale The Historic England Blog
Florence Nightingale - Nursing, Reform, Legacy: Although primarily remembered for her accomplishments during the Crimean War, Nightingale's greatest achievements centred on attempts to create social reform in health care and nursing. On her return to England, Nightingale was suffering the effects of both brucellosis and exhaustion. In September 1856 she met with Queen Victoria and Prince.
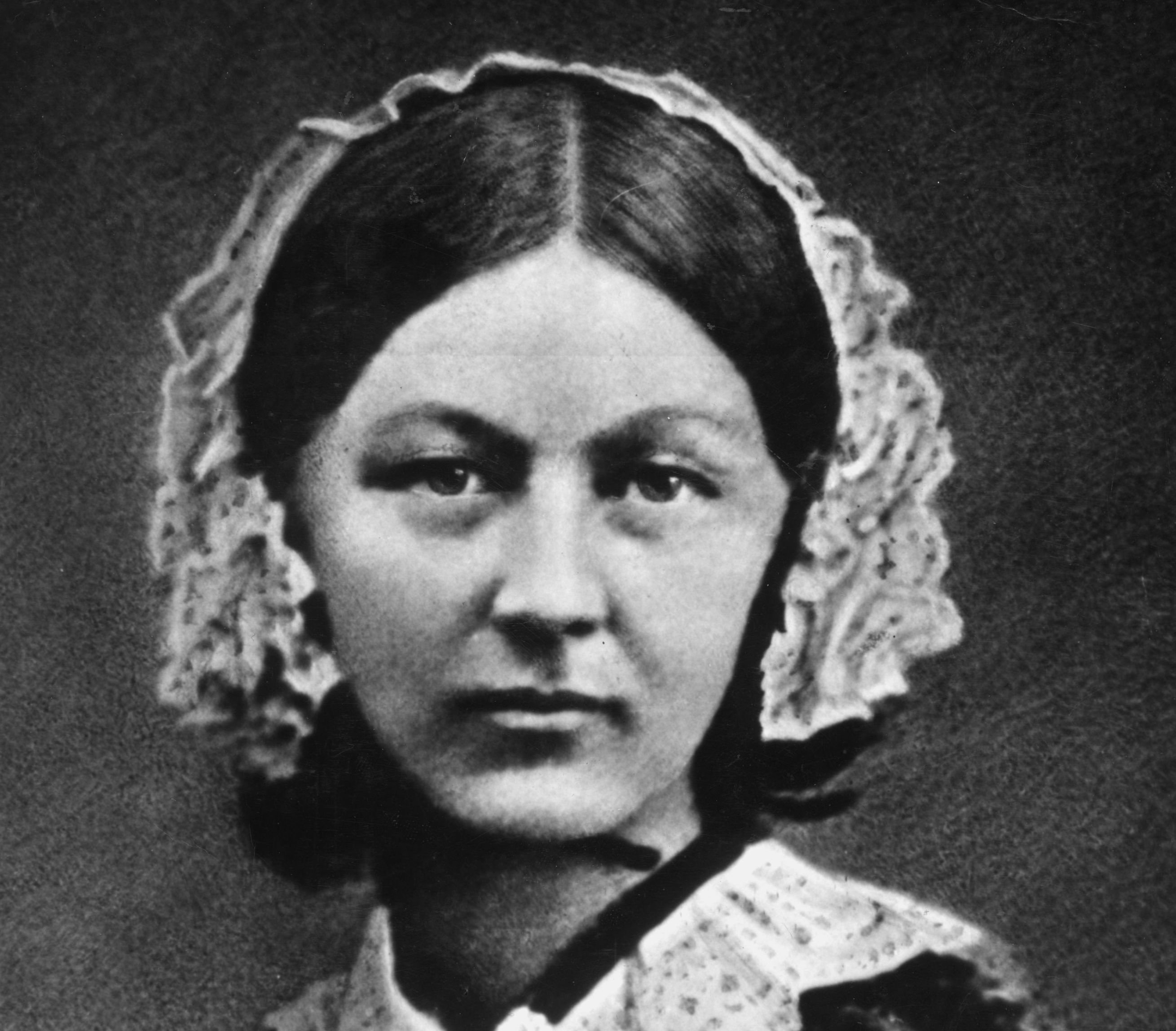

Quem foi Florence Nightingale A emocionante e inspiradora história de Florence Nightingale
May 12, 2020 5:42 AM EDT. W hen Greta Westwood was 4 years old, she read a children's book about Victorian nurse Florence Nightingale. Decades later, she still remembers being transfixed by the.

Who was Florence Nightingale? Twinkl
According to Florence Nightingale, hygiene, sanitation, fresh air, proper lighting, a good diet, warmth, quietness and attentiveness were necessary conditions for hospitals and were to be ensured by trained nurses. Taken for granted today, her commonsense advice helped transform hospitals from death houses to sanctuaries of care.
.jpg?auto=format%2Ccompress&fmt=webp)
Remembering Florence Nightingale on her Birth Anniversary
The Portrait of Florence Nightingale Florence from childhood loved God and holy Book. According to her, on the seventh of February 1837, while she was walking in a garden, she heard the voice of God, which was call her to a specific mission ( 1, 2 ). Florence in 1844 decided to work at the hospital. But, her parents were opposed to this idea.
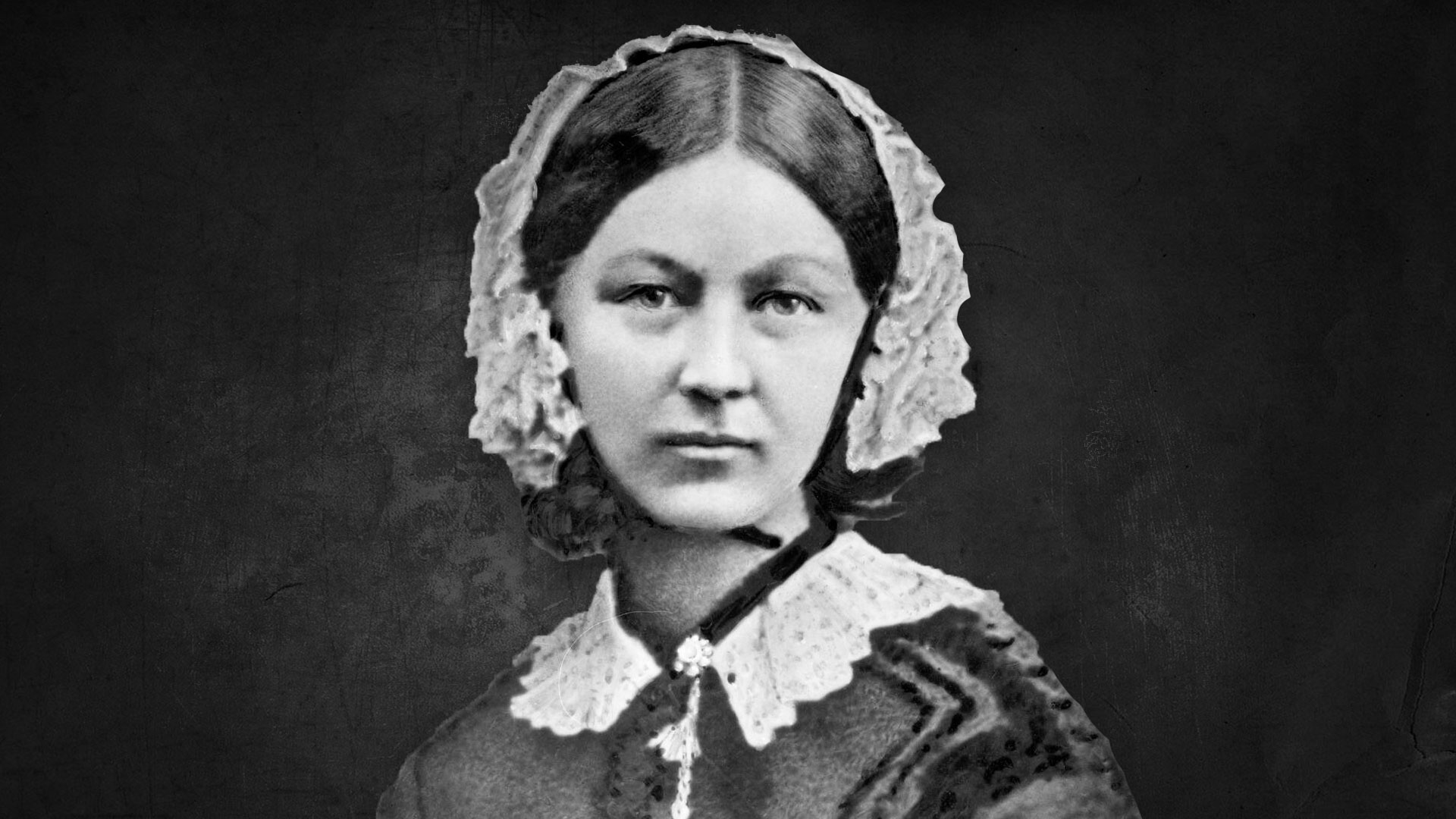
Florence Nightingale matemática, estadística y fundadora de la enfermería moderna
Florence Nightingale, (born May 12, 1820, Florence, Italy—died Aug. 13, 1910, London, Eng.), Italian-born British nurse, founder of trained nursing as a profession.As a volunteer nurse, she was put in charge of nursing the military in Turkey during the Crimean War.Her first concern was sanitation: patients' quarters were infested with rats and fleas, and the water allowance was one pint.