Die 4 Fälle im Deutschen alles über Nominativ Akkusativ Dativ Genitiv
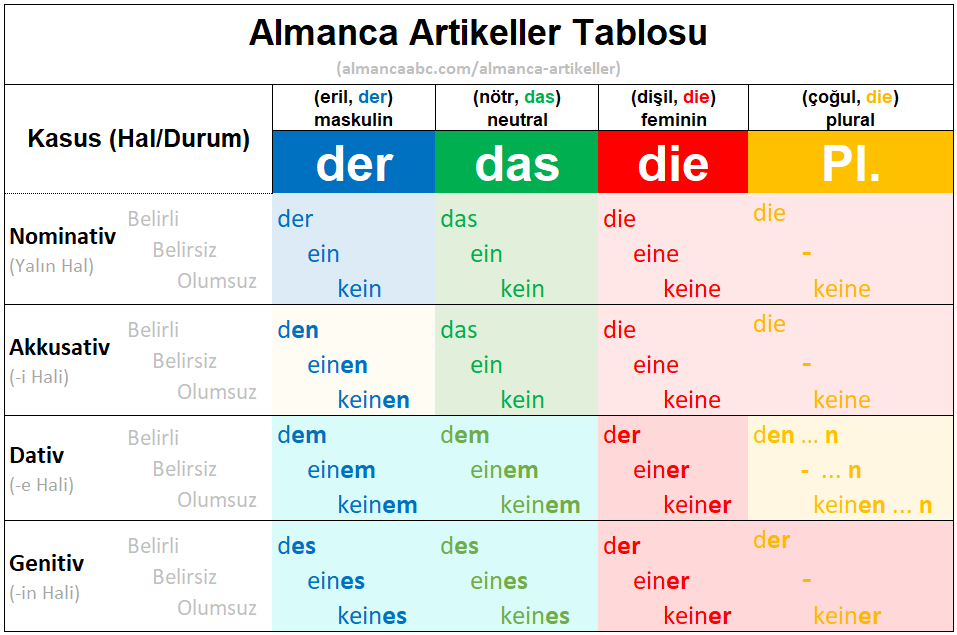
Dativ Nedir? Almanca İsmin e Hali Alan Fiiller & Örnek Cümleler
The German genitive case (Der Genitiv) The German genitive case is used to show possession and a few other relationships. The genitive tends to be found more in writing than in speech. Sometimes, you'll hear the dative case being used with the preposition von (of, from) to replace the genitive possessive.

Die Fälle Nominativ, Akkusativ, Dativ, Genitiv Genitiv, Grammatik, Deutsch lernen
Einleitung. Genitiv, Dativ und Akkusativ zu erkennen, ist für Deutschlernende oft nicht so einfach. Bestimmte Verben und Präpositionen im Deutschen verlangen einen bestimmten Fall. Vor allem die Anwendung von Dativ und Akkusativ ist oft ziemlich kompliziert. Mit der folgenden Übersicht lernst du ganz schnell, diese Fälle zu unterscheiden.

Overview Nominativ Genitiv Dativ Akkusativ Deutsch lernen, Deutsch, Lernen
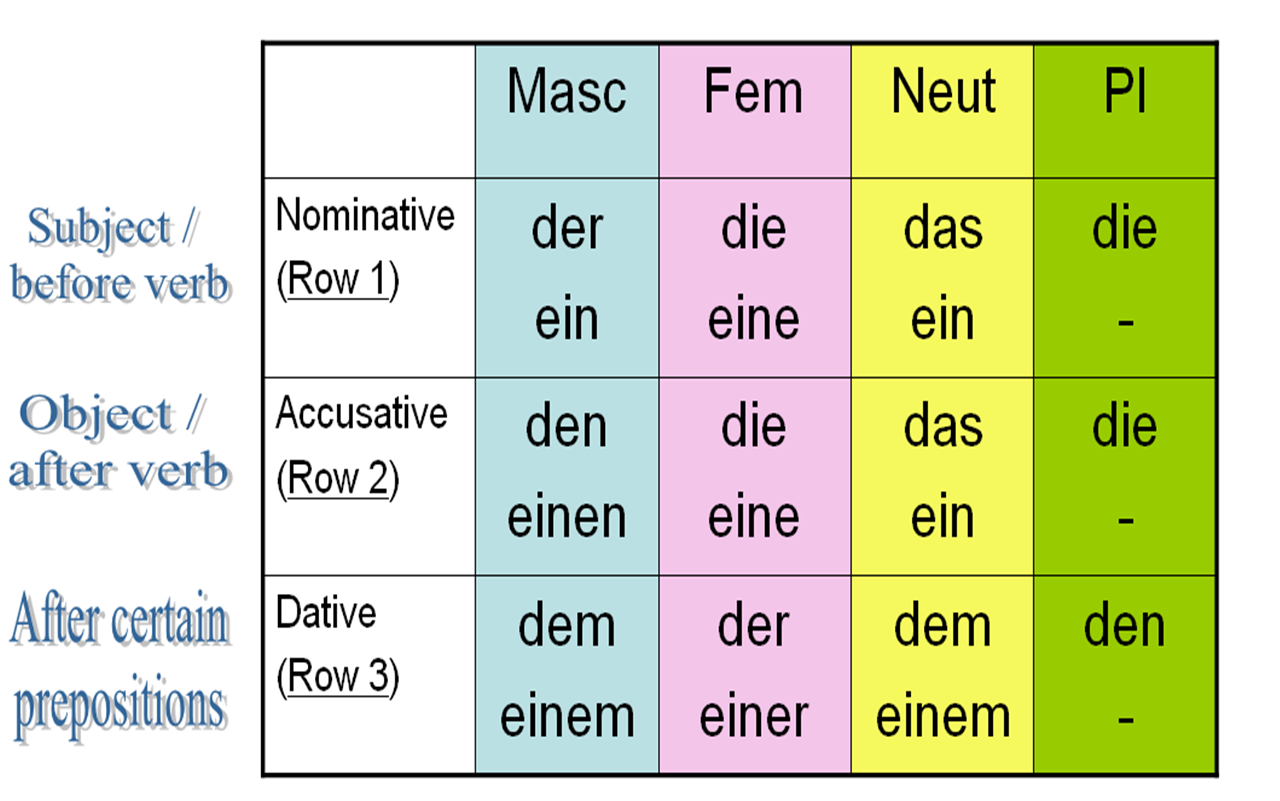
In German, there are four different forms or categories (cases), called Fälle or Kasus. Two of these cases are the nominative and the accusative. der Nominativ: The subject is always in the nominative case. The articles take the form: der/ein, die/eine, das/ein, die/-. der Akkusativ: Most objects are in the accusative case.

Nominativ Akkusativ Dativ Genitiv Deutsch Lernen
Akkusativ The accusative case. As you may have heard before, there are 4 grammar cases in German: nominative (Nominativ), accusative (Akkusativ), dative (Dativ) ,and genitive (Genitiv). Even though English does not have declensions, German cases have some correspondences with our English grammar features.

Die Fälle Nominativ, Akkusativ, Dati… Deutsch DAF Arbeitsblätter pdf & doc
German has only four cases, Nominativ, Genitiv, Dativ, Akkusativ. The names stem from latin and are basically the same as in other languages. The cases are usually numbered, so: Case: Nominativ / "Wer-Fall" From Latin nominare - to name sth. This case is used for the subject of a sentence. Case: Genitiv / "Wessen-Fall"
Nominativ , Akkusativ , Dativ
The Basics - Nominativ, Akkusativ oder Dativ? (Oder Genitiv?) To be able to follow this step-by-step guide you should have gone through all of the following topics already: The 4 German Cases (Nominative, Accusative, Dative und Genitive) Prepositions; Verbs with Complements; This guide is a summary of all the rules in a way that is easy to put.

Dativ, Akkusativ und Genitiv Deutsch Viel Spass
In diesem Video erkläre ich, wann wir Nominativ, Akkusativ, Dativ und Genitiv brauchen. Was ein Subjekt ist und wann wir zwei Mal den Nominativ im Satz haben.

Bildergebnis für nominativ genitiv dativ akkusativ tabelle Deutsch lernen, Genitiv, Nominativ
German Adjective Endings for the Nominative Case Definite and Indefinite Articles To further clarify what is happening here, take a look at the two German sentences below. What do you notice about the word grau ? 1. Das Haus ist grau. (The house is gray.) 2. Das graue Haus ist rechts. (The gray house is on the right.)
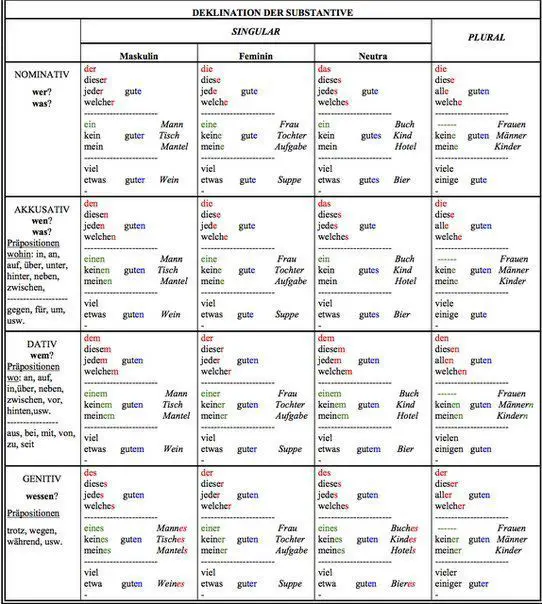
Nominativ, Akkusativ, Dativ und Genitiv die vier Fälle
What are German Cases? (Fälle / Kasus) German has "only" 4 cases: Which words can get a case (Kasus)? How to determine the case? The Four German Cases: Nominative (Nominativ) Accusative (Akkusativ) Dative (Dativ) Genitive (Genitiv) Summary German Cases: Exercises on the German Cases: Do you prefer to read this lesson German Cases in German?

Nominativ, Genitiv, Dativ und Akkusativ Deutsch Viel Spass
These cases are the nominative, accusative, dative and genitive cases. The nominative case is the subject of the sentence (" The cat is small. "). The accusative case is the direct object of it ( "I wear the hat. "). The dative is the indirect object, which is the receiver of the direct object. (" I give the hat to the woman.

Präpositionen Akkusativ Dativ Genitiv Dativ genitiv, Genitiv, Präpositionen
1. Fall: Nominativ Frage: Wer oder was? Der Pinguin steht auf der Eisscholle. 2. Fall: Genitiv Frage: Wessen? Das Gefieder des Pinguins ist sehr weich. 3. Fall: Dativ Frage: Wem? Dem Pinguin macht die Kälte nichts aus. 4. Fall: Akkusativ Frage: Wen oder was? Tina besucht den Pinguin oft im Zoo. Begleiter und Nomen verändern sich

Die vier Fälle Nominativ, Genitiv, Dativ, Akkusativ Lesbar
Depending on how a given word is used—whether it's the subject, a possessive, or an indirect or a direct object—the spelling and the pronunciation of that noun or pronoun changes, as does the preceding article. The four German cases are the nominative, genitive, dative, and accusative.

Artikel, der, die, das, den, dem, des, Nominativ, Akkusativ, Dativ, Genitiv, Tabelle, Beispiele
Akkusativ Dativ Genitiv Is there a way or technique - don't expect it to be accurate always - to know if a verb is of any of the types above or maybe it even belongs to more than 2 types? Any source on the internet or even a book recommendation would be helpful. verb grammatical-case reference-request Share Improve this question Follow

Dativ Akkusativ Erklärung (3. oder 4. Fall) Kostenloser Online Deutschkurs DeutschAkademie
Die Deklination hängt auch von Numerus (Singular oder Plural) und Genus (männlich, weiblich oder sächlich) des Nomens ab. Ein Nomen kann in vier Fällen (Kasus) stehen. Man kann diesen durch Fragen bestimmen. Fallbezeichnung | Fachbegriff | deutsche Bezeichnung | Frage 1. Fall | Nominativ | Wer-Fall | Wer oder Was? 2.

A1, A2, B1, B2, C1, Verwendung von Verben, Kasus, Wann Nominativ, Akkusativ, Dativ, Genitiv
Unter Kasus versteht man in der deutschen Sprache die vier Fälle: Nominativ. Genitiv. Dativ. Akkusativ. Diese 4 Fälle zeigen die Beziehung zwischen einem Nomen und anderen Elementen im Satz. Das Nomen in einem Satz steht also im Nominativ, Genitiv, Dativ oder Akkusativ. Das zeigt sich vor allem an den Artikeln und heißt Deklination .

Die 4 Fälle im Deutschen alles über Nominativ Akkusativ Dativ Genitiv
Das Genitivattribut. Das Deutsche hat vier Fälle: Nominativ, Akkusativ, Dativ und Genitiv. Mit dem Genitiv kann man Besitz oder Zugehörigkeit ausdrücken. Man kann ein Substantiv durch ein weiteres Substantiv im Genitiv, das Genitivattribut, ergänzen und damit erklären, wem oder zu was etwas gehört. Eigennamen stehen als Genitivattribut.