9 Sentences of Second Conditional, 9 Example Sentences Type 2 Conditionals English Study Here

CONDITIONAL CLAUSES / IF CLAUSES And its types (Type 0 , 1, 2 & 3 ) YouTube
If Clause Type 2 Form if + Simple Past, main clause with Conditional I (= would + Infinitive) Example: If I found her address, I would send her an invitation. The main clause can also be at the beginning of the sentence. In this case, don't use a comma. Example: I would send her an invitation if I found her address.

Conditionals 04 Types of Conditional Sentences in Grammar Efortless English
Lingolia Plus English Just here for the exercises? Click here. What is the second conditional? The second conditional, also type-II if-clause or the unreal conditional, talks about an unlikely or imaginary condition and its result. It imagines that the present is different to how it really is. Example:

First Second and Third Conditional, Example Sentences Table of Contents First ConditionalSecond
Form In a Type 2 conditional sentence, the tense in the 'if' clause is the simple past, and the tense in the main clause is the present conditional or the present continuous conditional.

If clauses English conditional clauses English in General
1. Use It is theoretically possible to fulfil a condition which is given in the if-clause. 2. Form 3. Examples The if-clause can be at the beginning or at the end of a sentence. Mind the comma. if I were you or if I was you if - Omitting if - if vs. when - in case vs. if will and would in if-clauses You are here:

9 Sentences of Second Conditional, 9 Example Sentences Type 2 Conditionals English Study Here
The conditional type 2 refers to an unlikely or hypothetical condition and its probable result. These sentences are not based on the actual situation. In conditional type 2 sentences, the time is now or any time and the situation is hypothetical. EXAMPLES If the weather wasn't so bad, we would go to the park.

Second conditional sentence (ifsentence type 2) English in General
Conditional Sentence Type 1 → It is possible and also very likely that the condition will be fulfilled. Form: if + Simple Present, will-Future Example: If I find her address, I'll send her an invitation. more on Conditional Sentences Type I Conditional Sentence Type 2 → It is possible but very unlikely, that the condition will be fulfilled.

English Conditional Sentences, If Clauses Type 0, Zero Conditional If clauses are conditional
The Simple Past Tense is generally used for the tense structure of the clause using "if". Sometimes the Past Continuous Tense can also be used. "Would", "Could" and "Might" are used for the structure of the main sentence. Examples for Conditionals Type 2. Examining the examples given for If Clause Type 2 can help reinforce the.
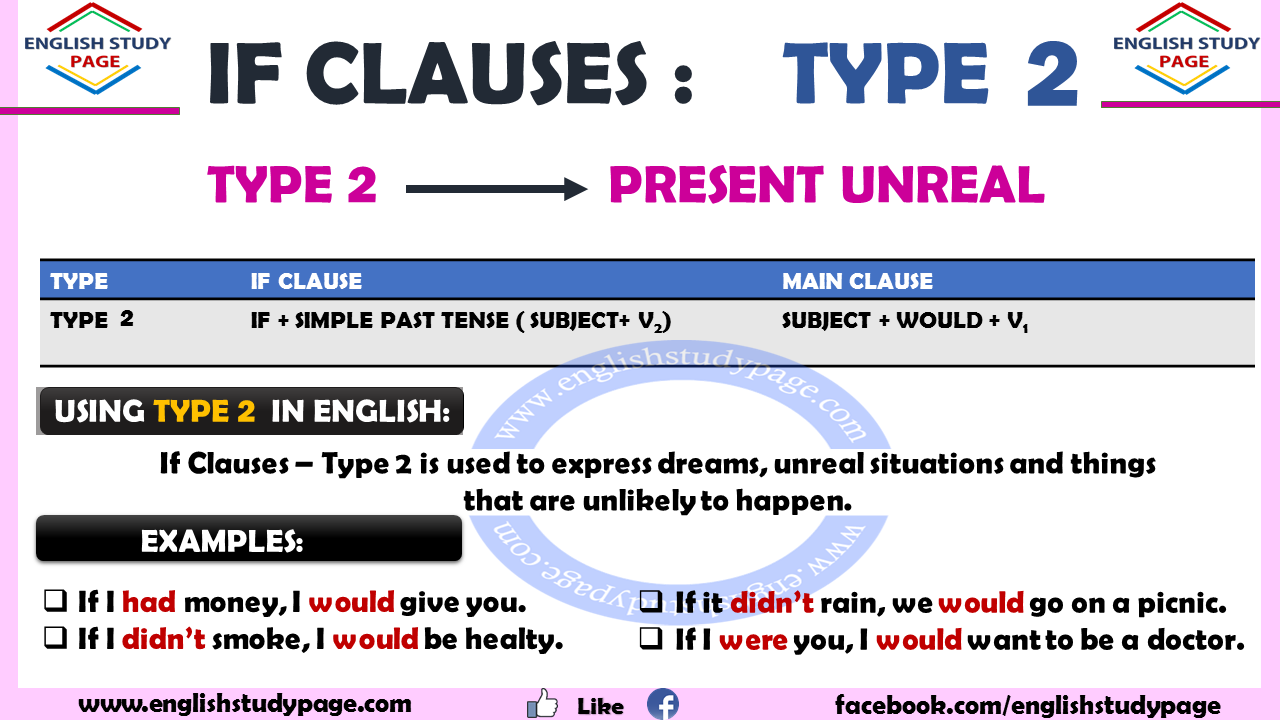
If Clauses Type 2 English Study Page
Conditionals Type 2 statements refer to things that don't happen, or even that is unlikely to happen. In other words, the condition you have stated in these sentences does not express the real situations, it refers to the situations you imagine at that moment.

Conditional Sentences Typ 2 if clauses Englisch üben
If Clauses - Type 2 is used to express dreams, unreal situations and things that are unlikely to happen. In other words, The condition specified in the clause is not actual but is a condition that is currently being imagined. Although the verb is used in the past, we use type 2 when talking about present time or now. Examples:

Result Clause Conditional Sentence FEQTUCA
Grammar explanation Conditionals describe the result of a certain condition. The if clause tells you the condition ( If you study hard) and the main clause tells you the result ( you will pass your exams ). The order of the clauses does not change the meaning. If you study hard, you will pass your exams. You will pass your exams if you study hard.
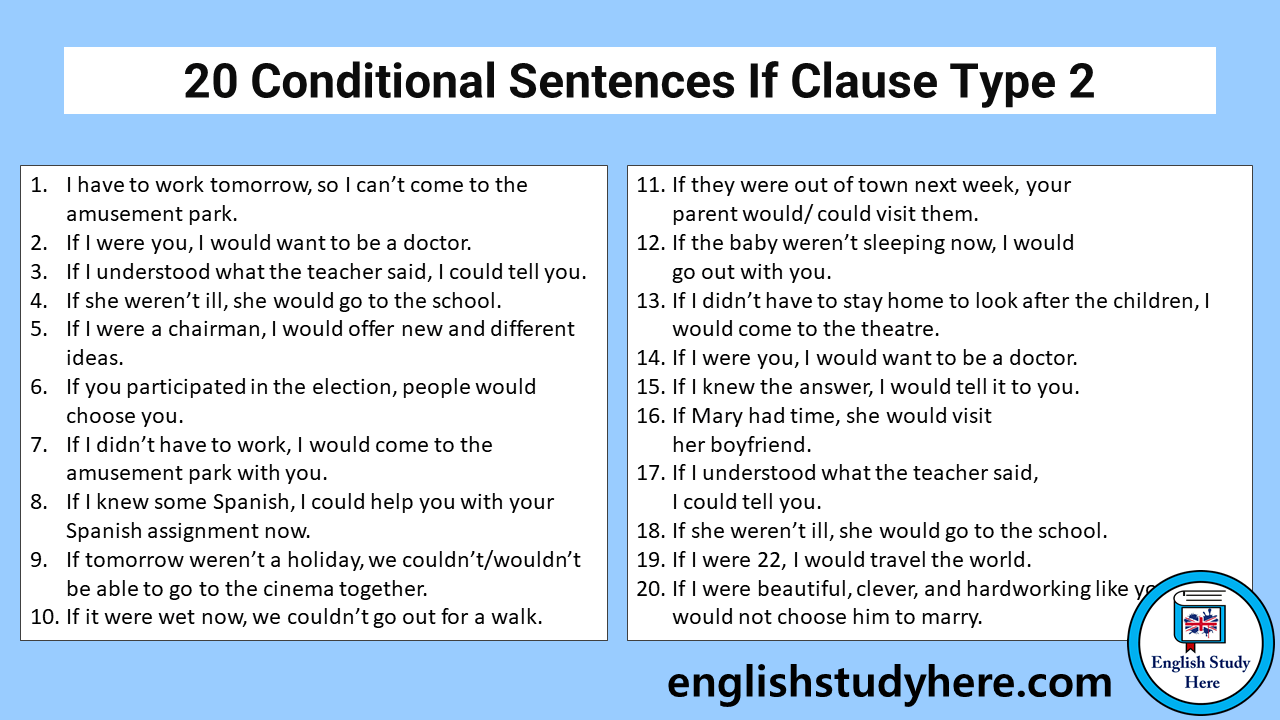
Conditionals Archives English Study Here
If Clauses | Type 2 Conditional. Here we use a simple past in the if-clause and would + infinitive (bare form of the verb) in the result clause. If you asked, they would help you. If it rained, you would get wet. If you loved her, she would love you. If I had more money, I would buy a new car. If he studied more, he would pass the exam.

30 Second Conditional Sentences Examples, If Clauses Type 2 English Vocabs
What Is the Second Conditional? Learn how and when to use Conditional Sentences Type 2 (Present Unreal Conditional) with useful form, usage and example sentences. Like a first conditional, a second conditional sentence consists of two clauses, an 'if' clause and a main clause. We use different verb forms in each part of a 2nd conditional:

Conditional Sentences Exercises Type 1 And 2 And 3 Exercise Poster
A type 2 conditional sentence, also known as the second conditional sentence, refers to a condition (situation) that is impossible or unlikely to be true (in the present), and its result in the present or near future (very close to the present). We employ second conditional sentences when we want to talk about something that is opposite to reality.
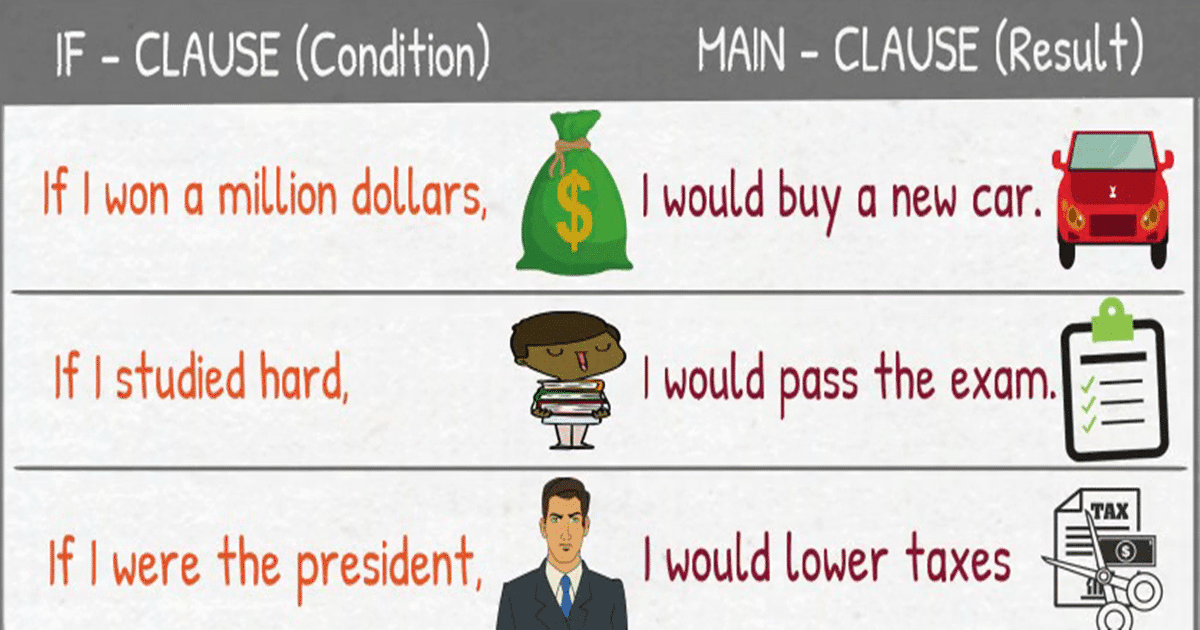
English Grammar Second Conditional
Which type of conditional sentences is it? Where is the if-clause (e.g. at the beginning or at the end of the conditional sentence)? There are three types of conditional sentences. 1. Form 2. Examples (if-clause at the beginning) Mind the comma after the if clause. 3. Examples (if-clause at the end) 4. Examples (affirmative and negative sentences)

Conditional Sentences Type 1 Conditional sentence, Types of sentences, English study
English grammar Conditional sentences ( if clauses) Second conditional ( if -clause type 2) if -clause type 2 (second conditional) (Explanation of conditional sentences type 2 in English) Table of contents - second conditional On this page you will find the following: Use of the second conditional sentence Form of the second conditional sentence

If Clause Table, Type 0,1,2,3 English language learning grammar, Conditionals grammar
English Conditional Sentences, If Clause Type 2, Conditional Type 2 TYPE 2: UNTRUE IN THE PRESENT OR FUTURE If Clause Type 2 is used to think of the opposite of an event that is happening in the present or in the future, to put forward a condition and to express the result of this imaginary condition. Therefore, the tense that we can use must be a bit more past than the tense that we will use.